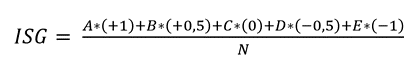
Cooperativismo y Desarrollo, May-August 2024; 12(2), e669
Translated from the original in Spanish
Original article
Environmental education strategy for local development
Estrategia de educación ambiental para el desarrollo local
Estratégia de educação ambiental para o desenvolvimento local
Evelyn Pérez Rodríguez1  0000-0002-4273-9335
0000-0002-4273-9335  evelyn@upr.edu.cu
evelyn@upr.edu.cu
Elisa Maritza Linares Guerra1  0000-0002-6333-867X
0000-0002-6333-867X  maritza.linares@upr.edu.cu
maritza.linares@upr.edu.cu
Dora Lilia Márquez Delgado1  0000-0003-0060-0455
0000-0003-0060-0455  doraly@upr.edu.cu
doraly@upr.edu.cu
Raymundo Vento Tielve1  0000-0002-1480-7783
0000-0002-1480-7783  tielve@upr.edu.cu
tielve@upr.edu.cu
1 University of Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saíz Montes de
Oca". Center for the Study of the Environment and Natural Resources. Pinar del Río, Cuba.
Received: 23/10/2023
Accepted: 18/07/2024
ABSTRACT
The interrelation between community environmental education and local development
prepares the individual to be able to improve his or her relationship with the natural environment, and
thus the way of thinking and acting. The purpose of this work was to design strategic actions
of environmental education for the local development of the "Alvarito Díaz" community,
highlighting the links that make possible a socially responsible action in the natural environment, with a
view to sustainable local development. A descriptive observational study was carried out with
the application of theoretical and empirical methods, and the application of the SWOT matrix
to obtain a general perspective of the local situation. As a result, an environmental strategy
was designed with a series of elements based on the system approach, which proposes actions
to develop strengths, reduce weaknesses, locate and take advantage of opportunities and
reduce the threats encountered. Its design had a high level of satisfaction on the part of the users
to provide new ways to generate significant changes in behavior and development through
training and education of the different social actors.
Keywords: community; local development; environmental education; strategy.
RESUMEN
La interrelación educación ambiental comunitaria y el desarrollo local prepara al individuo
para que sea capaz de mejorar su relación con el entorno natural, y así la forma de pensar y actuar.
El presente trabajo tuvo como propósito diseñar acciones estratégicas de educación ambiental
para el desarrollo local de la comunidad "Alvarito Díaz", destacando los nexos que posibilitan
una actuación socialmente responsable en el entorno natural, con una mirada al desarrollo
local sostenible. Se realizó un estudio observacional descriptivo con la aplicación de métodos
teóricos y empíricos, y la aplicación de la matriz DAFO para obtener una perspectiva general de la
situación local. Como resultado se diseñó una estrategia ambiental que en su composición cuenta con
una serie de elementos que se fundamentaron desde el enfoque de sistema, lo que propone
acciones para desarrollar fortalezas, reducir las debilidades, localizar y aprovechar las oportunidades
y disminuir las amenazas encontradas. Su diseño tuvo un elevado nivel de satisfacción por parte
de los usuarios para proporcionar nuevas maneras de generar cambios significativos
de comportamiento y de desarrollo mediante la capacitación y la formación de los diferentes
actores sociales.
Palabras clave: comunidad; desarrollo local; educación ambiental; estrategia.
RESUMO
A inter-relação entre a educação ambiental comunitária e o desenvolvimento local prepara
o indivíduo para ser capaz de melhorar sua relação com o ambiente natural e, portanto, sua
forma de pensar e agir. O objetivo deste trabalho foi projetar ações estratégicas de educação
ambiental para o desenvolvimento local na comunidade "Alvarito Díaz", destacando os vínculos que
permitem uma ação socialmente responsável no ambiente natural, com vistas ao desenvolvimento
local sustentável. Foi realizado um estudo observacional descritivo com a aplicação de métodos
teóricos e empíricos e a aplicação da matriz SWOT para obter uma visão geral da situação local.
Como resultado, foi elaborada uma estratégia ambiental com uma série de elementos baseados
na abordagem sistêmica, que propõe ações para desenvolver os pontos fortes, reduzir os
pontos fracos, localizar e aproveitar as oportunidades e reduzir as ameaças encontradas. Sua
concepção teve um alto nível de satisfação dos usuários por proporcionar novas maneiras de gerar
mudanças significativas no comportamento e no desenvolvimento por meio da capacitação e do
treinamento dos diferentes atores sociais.
Palavras-chave: comunidade; desenvolvimento local; educação ambiental; estratégia.
INTRODUCTION
The wide range of environmental problems affecting the planet
has been influenced by a lack of environmental awareness and education in a considerable percentage of the population and
has resulted, on many occasions, in their aggravation (Rodríguez García & Peña Fuentes, 2019), so
it requires the mobilization of all actors to face the challenge and jointly formulate responses to
the problems. All this requires developing in people's minds a new way of looking at the
environment, by educating conceptually and attitudinally to contribute to the development of a
positive environmental quality through the solution of environmental problems at the local level
(Sánchez Santamaría et al., 2010).
An alternative to obtain the participation of the population in the solution of environmental
problems in their own environments consists of environmental education, as it is key to understand
the existing relationships between the contexts of nature, society and economy, as well as to
achieve a more evident perception of the importance of socio-cultural factors in the genesis of
environmental problems (Orihuela & Paredes, 2015).
In the search for tools aimed at curbing or, at least, mitigating the deterioration of the
environment, is that environmental education arises, in order to achieve the participation of social
actors, united with organizations and institutions in pursuit of a new conservationist ethic from
the development of a comprehensive educational process (Acevedo Rodríguez et al., 2019).
Environmental education is important in promoting sustainable development and increasing
the capacity of populations to address environmental development issues, using academic and
non-academic methods and effective means of communication. The environmental issue is
currently a challenge of global commitment to the protection of natural resources (Martínez Castillo,
2012). In this way, environmental education is valued as a process and a factor of social change,
which coincides with the aim of achieving sustainable development (De la Peña Consuegra &
Vinces Centeno, 2020).
Environmental education and local development are two important and topical terms in
the framework of sustainable development. Environmental education is a strategic factor that
affects the established forms of development in order to reorient them towards sustainability and
equity, thus building a new lifestyle (Pérez Díaz et al., 2019). Community work constitutes the
scenario where the protagonism of local actors in the search for solutions to their own problems must
be achieved (Bustio Ramos, 2023).
The study of local development should not be separated from environmental education
since human beings develop their lives in a complex social reality and, from this, it follows that
an educational process is necessary to address all aspects of environmental problems
(Hernández Martín et al., 2021).
This is an important element to take into account for local development; each of the
dimensions mentioned above contributes in an integral way to the improvement of the living conditions of
the inhabitants and favors the promotion of this, in a more favorable environment, with the use
of endogenous resources (Sosa González et al., 2020).
This research focuses on one of the aspects of local development, the environmental
component, and its objective is to design strategic environmental education actions for the local
development of the "Alvarito Díaz" community in the municipality of Consolación del Sur, Pinar del Río province.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A technological development research was carried out in the "Alvarito Díaz" community of
the "Puerta de Golpe" popular council in the municipality of Consolación del Sur (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Satellite location of the community "Alvarito Díaz"
Source: Physical Planning Pinar del Río
To determine the environmental problem in the community, the environmental
diagnosis methodology proposed by Linares Guerra et al. (2021) was applied, which has six stages:
- Identification of information needs
- Definition of the sources of information, methods, procedures and techniques to be used
- Design of the formats for the collection of information according to the techniques
defined above
- Sample size determination
- Data collection, processing and analysis
- Conclusion of the environmental diagnosis
The following methods were used to design the strategy:
- The modeling method that allowed us to build the strategy of the environmental
education process in the studied community.
- The structural systemic method, which made possible the general orientation for the
design and substantiation of the proposal, by facilitating the determination of the components
of the strategy through the relationships that make it up, as well as its structure.
- The ethnographic method that allowed the capture of the community's way of life,
its social structure and the process of development of environmental education in
the inhabitants.
- The participatory action research method allowed the understanding and interpretation
of the environment in the community under study and the development in its inhabitants
of a critical awareness of their own needs, problems and ways to solve them.
- The Iadov Method was used as a scientific methodological procedure for processing
the results. This technique constitutes an indirect way for the study of customer
satisfaction (Mirabal Sarria & Torres Paez, 2021) to estimate the level of satisfaction of the
inhabitants of the "Alvarito Díaz" community with the proposed environmental education
strategy. The technique was applied to 10 inhabitants of the locality that are part of the
universe, four formal leaders, three informal leaders and three members of the locality, of
which 60% belong to the female gender and 40% to the male gender.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The "Alvarito Díaz" community is a hamlet in the municipality of Consolación del Sur, with
a predominance of agricultural production and, irregularly, fishing. It has an
extension of 2 km2 , it is located at kilometer 3½ of the Central Highway that leads to the Popular Council Puerta
de Golpe, 11.5 km west southwest of the municipal capital and linked to it by road, at 22° 28' 15"
N latitude and 84° 35' 12" West longitude, in the southern plains of Pinar del Río (Cabeza Defaus
& Jaula Botet, 2022).
Based on the analysis of the instruments (Observation Guide) used for the environmental
diagnosis, the following environmental problems are regularly identified:
- Deforestation
- Disappearance of plants and animals that once existed in the community
- Inefficient solid waste management
- The deplorable sanitization of backyards in homes
- Soil degradation due to agricultural activity
- Family conflicts
- Violent behaviors
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages
- Poor housing conditions
- Lack of drinking water
- Overcrowded housing
These identified environmental problems are recognized by several actors who have studied
rural communities, such is the case of Pérez Rodríguez et al. (2018). These problems are caused
by humans to the environment, through the irrational use of natural resources and the emergence
of conflicts that exacerbate social problems.
Based on the diagnosis of the main environmental problems, insufficient environmental
education is recognized as the main problem, making it necessary to implement an environmental
education instrument to help mitigate or solve these problems.
In the elaboration of the strategy, the structure and characteristics of the community were
taken into account in order to carry out, in a comprehensive and flexible manner, a set of
systematic and coherent actions in its development.
The environmental education strategy proposed for the "Alvarito Díaz" community in
the municipality of Consolación del Sur, in Pinar del Río, was structured in five stages, the same
as the one designed by Pérez Díaz et al. (2019), as shown in the following scheme:
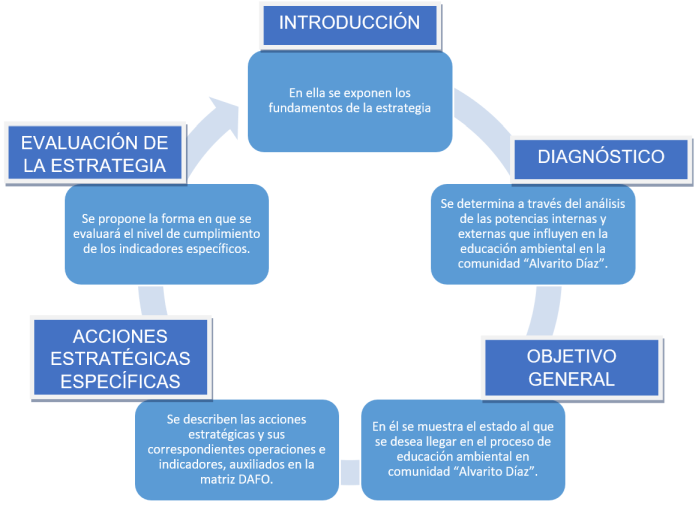
Figure 2. Structure of the environmental education strategy in the community "Alvarito Díaz"
Source: Own elaboration
Strategy structure
Introduction
The strategy was designed to mitigate environmental deterioration and strengthen
the environmental education process, with the participation of social actors, together with
organizations and institutions in order to achieve local community
development. It consists of a set of elements based on the system approach,
where the inhabitants of the community will be the
protagonists of the actions that are developed in it, from the incorporation of the actors in the decision
making to carry out the process of environmental education from the community sociocultural work.
Diagnosis to implement the environmental education strategy in the community
The preparation of the SWOT matrix (a technique used to identify weaknesses, threats,
strengths and opportunities) contains a series of internal and external forces that have a direct impact
on the development of actions to develop strengths, reduce weaknesses, locate and take
advantage of opportunities and reduce or avoid the threats encountered. It is a tool that allows obtaining
a clear diagnosis to make strategic decisions in a timely manner and improve in the future
(Peñafiel Nivela et al., 2020).
In order to obtain internal and external forces, group interviews were carried out, which led to
the identification of positive and negative elements, both inside and outside the community.
These elements are closely linked to environmental problems and the process of environmental
education in the locality.
- Internal forces
- Strengths
- The People's Council is structured and organized in a way that favors the
introduction and development of the environmental education strategy in the "Alvarito
Díaz" community.
- The community is willing to work on the solution of environmental problems
that have been identified from the genesis, formulation, evaluation and follow-up of
the actions to be developed.
- Existence of the community project "El Patio de Pelegrín" in the popular council
to which the community belongs.
- Weaknesses
- Lack of an environmental education strategy for the community that would lead
to the improvement of the current environmental situation.
- There is a partial and asystemic treatment of the elements linked to the
knowledge, perception and sensitivity of the population to environmental problems in the
locality without projecting solutions towards know-how.
- There are insufficiencies in the joint coordination of environmental education
actions that contribute to responsible environmental behavior.
- Unstable and insufficient levels of communication, commitment and
integration (mass and interpersonal) on environmental problems and their solutions.
- External forces
- Opportunities
- Support from political and mass organizations.
- Existence of a Municipal Government identified with the environmental
problems of the community.
- Creation of a promoter or facilitator group in the community itself to carry out
and sustain the training processes, strategies and projects in the
environmental transformation of the community.
- Participation of the provincial and municipal mass media.
- Threats
- Difficult economic conditions in the country.
- Lack of material resources for community development.
- Insufficient environmental education actions from the institutional level to
strengthen knowledge, skills and attitudes of the subjects regarding the care and protection of
the environment.
- Impacts caused by the COVID 19 pandemic.
Objective of the strategy: To manage environmental education from a systemic and
integral approach to local development that contributes to the improvement of the environmental
situation in the "Alvarito Díaz" community.
Specific strategic actions (Table 1)
Table 1. Summary of the environmental education strategy in the community "Alvarito Díaz"
Strategic actions |
Activities |
Indicators |
To identify the needs of the community environmental education process in the "Alvarito Díaz" community with a holistic, multidisciplinary and intersectorial approach. |
- Survey to determine the main environmental problems and the effects they cause in the "Avarito Díaz" community, by formal and non-formal leaders.
- Development of workshops to socialize the results found in the identification of the main problems.
|
- Level of awareness of the need for change in the environmental education process to which the inhabitants of the community have been led on the priority of generating new attitudes for the resolution of the environmental problems to be identified.
|
To train through community participatory activities that promote the successful solution of environmental problems in the "Alvarito Díaz" community. |
- Training of the facilitator group and formal and non-formal community leaders on environmental education.
- Lectures given by specialists of the Territorial Delegation of the Ministry of Science, Technology and Environment in the territory on environmental education and the methods to be used to solve the problems that were detected.
- Workshops with the community to analyze possible solutions to their main environmental problems.
|
- Level of assistance and empathy of the inhabitants of the "Alvarito Díaz" community in the development of the planned training activities.
- Proposals for solutions to mitigate the environmental problems detected.
|
To develop voluntary and participative actions for the transformation of environmental problems in the "Alvarito Díaz" community. |
- Reforestation actions with endemic species.
- Elimination of micro dumps.
- Selection of Sustainable Courtyards.
- Creation of a rural and sustainable vegetable garden for local supply.
- Reflect on the changes that occur in the community once the environmental problems have been solved.
|
- Attitude of the villagers towards the operations to be carried out in favor of community environmental management.
- Amount of reforested area.
- Community integration) in the activities developed (90% of the inhabitants of the locality.
- Increase in the quality of life of the community.
|
Promote environmental education activities aimed at solving environmental problems in the "Alvarito Díaz" community. |
- Creation of scenarios where the different environmental problems are disseminated in the community.
- Dissemination of solutions to environmental problems.
- Exhibition of different artistic manifestations linked to the El Patio de Pelegrín Project on the theme of the environment.
- Organization of a gallery of images of the community related to the environmental education activities they carry out.
|
- Increased community motivation towards environmental education activities and mitigation of environmental problems.
|
Source: Own elaboration
Strategy evaluation
In this evaluation stage of the environmental education strategy in the community under
study, it will be developed in a pleasant and flexible way, visualized as a phase that occurs
naturally during the process. In it, the analysis of the objectives of the proposed indicators, which have
a direct impact on the efficiency, effectiveness, preservation and relevance of the strategy,
should be deepened.
The evaluation process will give the strategy a greater validity, from its revision, updating
and readjustment, with the purpose of making it a useful product for the improvement of
the environmental education process in the "Alvarito Díaz" community, as an instrument
of transformation.
Results obtained in the validation of the environmental strategy
In the present research, the Iadov technique was applied as an indirect way to study
satisfaction, since the criteria used are based on the relationships established between three closed
questions that are inserted in a questionnaire and whose relationship is unknown to the subject.
These three questions are related through what is called Iadov's Logical Table (Table 2).
Table 2. Iadov's logic table
Question 3. Do you like the way the environmental education strategy was designed and structured for the community? |
Question 2. Do you feel satisfied with the environmental education strategy designed for the "Alvarito Díaz" community? |
Yes |
No |
I do not know |
Question 6. Do you consider that the environmental strategy designed for the "Alvarito Díaz" community responds to the mitigation of the environmental problems existing in the community? |
Yes |
No |
I do not know |
Yes |
No |
I do not know |
Yes |
No |
I do not know |
a) I like it very much |
1 |
2 |
6 |
2 |
2 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
b) I like it more than I dislike it |
2 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
6 |
c) I am indifferent |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
d) I dislike it more than I like it |
6 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
e) I do not like |
6 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
4 |
4 |
6 |
4 |
5 |
f) I cannot say |
2 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
4 |
Source: Own elaboration
By applying the method and performing the corresponding analysis between the questions
contained in the table, it was possible to obtain the individual satisfaction level of each community
member surveyed, as shown in figure 3.
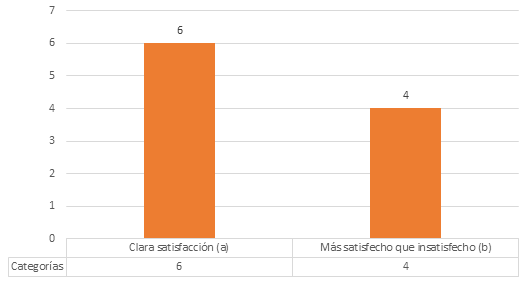
Figure 3. Level of satisfaction of the inhabitants of the "Alvarito Díaz" community with
the environmental education strategy
Source: Own elaboration
In calculating the Global Satisfaction Index (GSI), the formula was used:
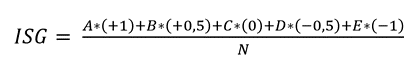
Where N = total number of respondents.
For this purpose, the values obtained in the categories of A = 6; B = 4; C = 0; D
= 0 and E = 0 were substituted, obtaining an ISG = 0.8. According to the scale, the result is satisfactory as it
is within the value range of 0.5 -+ 1 (Figure 4).
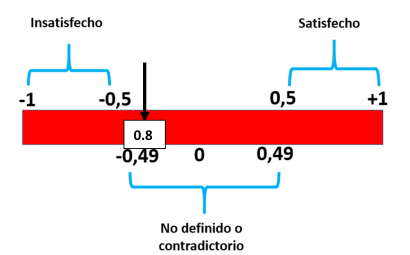
Figure 4. Interpretation of the ISG according to the scale
Source: Own elaboration
The design of strategic environmental education actions in the "Alvarito Díaz" community, as
well as their implementation with community participation constituted a dynamic, conscious
and reflexive process, in response to local development and the promotion of favorable changes in
the lifestyle of its inhabitants.
The satisfactory validation obtained by user criteria reinforces the theoretical and practical
value of the strategy whose implementation provides the management of the environmental
education process in the community.
REFERENCES
Acevedo Rodríguez, C., García Alonso, A., & Pérez Cruz, I. (2019). La educación
ambiental desde la metodología del autodesarrollo comunitario en los pobladores de la
Comunidad Marinera Castillo de Jagua. Universidad y
Sociedad, 11(3), 274-281.
https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/1255
Bustio Ramos, A. (2023). El Trabajo Comunitario Integrado y su incidencia en el
desarrollo local. Cooperativismo y
Desarrollo, 11(2), e642.
https://coodes.upr.edu.cu/index.php/coodes/article/view/642
Cabeza Defaus, N., & Jaula Botet, J. A. (2022). Diagnóstico inicial. Estrategia de
educación ambiental en la comunidad «Alvarito Díaz», Consolación del Sur, Cuba. Revista ECOVIDA, 12(2), 152-159. https://revistaecovida.upr.edu.cu/index.php/ecovida/article/view/252
De la Peña Consuegra, G., & Vinces Centeno, M. R. (2020). Acercamiento a
la conceptualización de la educación ambiental para el desarrollo sostenible. Revista Cubana de Educación Superior,
39(2). https://revistas.uh.cu/rces/article/view/2182
Hernández Martín, J. C., Reinoso Castillo, I., & Rodríguez García, R. M. (2021).
Educación ambiental comunitaria y desarrollo local. Un binomio imprescindible en la época
actual. Didáctica y Educación,
12(3), 83-93. https://revistas.ult.edu.cu/index.php/didascalia/article/view/1163
Linares Guerra, E. M., Díaz Aguirre, S., González Pérez, M. M., Pérez Rodríguez, E., &
Córdova Vázquez, V. (2021). Metodología para el diagnóstico ambiental comunitario con
fines investigativos desde el posgrado académico. Universidad y Sociedad, 13(4), 309-319.
https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/2170
Martínez Castillo, R. (2012). Ensayo crítico sobre educación ambiental. Revista Electrónica Diálogos
Educativos, 12(24), 74-104. http://revistas.umce.cl/index.php/dialogoseducativos/article/view/1056
Mirabal Sarria, Y., & Torres Paez, C. C. (2021). Validación del modelo de gestión pública de
la calidad de vida en Cuba. Cooperativismo y
Desarrollo, 9(3), 919-934. https://coodes.upr.edu.cu/index.php/coodes/article/view/453
Orihuela, J. C., & Paredes, M. (2015). Gestión sostenible de recursos naturales e
industrias extractivas: Los desafíos del desarrollo regional basado en recursos
extractivos. Consorcio de Investigación Económica y Social (CIES). https://cies.org.pe/investigacion/gestion-sostenible-de-recursos-naturales-e-industrias-extractivas-los-desafios-del-desarrollo-regional-basado-en-recursos-extractivos/
Peñafiel Nivela, G. A., Acurio Armas, J. A., Manosalvas Gómez, L. R., & Burbano Castro, B.
E. (2020). Formulación de estrategias para el desarrollo empresarial de la constructora
Emanuel en el cantón La Maná. Universidad y
Sociedad, 12(4), 45-55.
https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/1611
Pérez Díaz, N., Suero Gutiérrez, L., Veliz Gutiérrez, J. Á., Linares Guerra, E. M., &
Pérez Rodríguez, E. (2019). Acciones estratégicas de educación ambiental en la comunidad
La Majagua para su desarrollo local. Cooperativismo y
Desarrollo, 7(3), 406-419. https://coodes.upr.edu.cu/index.php/coodes/article/view/273
Pérez Rodríguez, E., Linares Guerra, E. M., Márquez Delgado, D. L., Vento Tielve, R., &
Pérez Díaz, N. (2018). Evaluación de indicadores de sostenibilidad en la comunidad "Los
Jazmines", Viñales, Pinar del Río, Cuba. Revista Brasileira de Planejamento e
Desenvolvimento, 7(5), 732-754. https://doi.org/10.3895/rbpd.v7n5.8918
Rodríguez García, A., & Peña Fuentes, L. (2019). La protección del medioambiente en
Cuba, una prioridad gubernamental. Novedades en
Población, 15(30), 113-122.
https://revistas.uh.cu/novpob/article/view/558
Sánchez Santamaría, A. G., González González, M., Dueñas Bravo, N., & Corrales Valdés, R.
J. (2010). Programa de educación ambiental no formal en comunidades rurales: Una
experiencia cubana. Revista Digital Sociedad de la
Información, (22), 1-9. http://www.sociedadelainformacion.com/22/cub.pdf
Sosa González, M., Riquelme Rivero, Y., & Diez Valladares, O. R. (2020). Consideraciones
sobre el desarrollo local. Universidad y
Sociedad, 12(4), 309-315.
https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/1649
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Authors' contribution
Evelyn Pérez Rodríguez and Raymundo Vento Tielve participated in the conception, design and writing of the draft of the study.
Elisa Maritza Linares Guerra and Dora Lilia Márquez Delgado participated in data collection, analysis and interpretation.
All the authors reviewed the writing of the manuscript and approve the version finally submitted.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
 0000-0002-4273-9335
0000-0002-4273-9335  evelyn@upr.edu.cu
evelyn@upr.edu.cu 0000-0002-6333-867X
0000-0002-6333-867X  maritza.linares@upr.edu.cu
maritza.linares@upr.edu.cu 0000-0003-0060-0455
0000-0003-0060-0455  doraly@upr.edu.cu
doraly@upr.edu.cu 0000-0002-1480-7783
0000-0002-1480-7783  tielve@upr.edu.cu
tielve@upr.edu.cu