 0000-0002-7380-6115
0000-0002-7380-6115  tdsama1991@gmail.com
tdsama1991@gmail.comEduardo Iglesias Fidalgo2
 0009-0005-7853-6846
0009-0005-7853-6846  acerco@nauta.cu
acerco@nauta.cuViviana Sánchez Muñoz2
 0009-0002-1331-8766
0009-0002-1331-8766  viviana.acerco@gmail.com
viviana.acerco@gmail.com
Cooperativismo y Desarrollo, September-December 2023; 11(3), e572
Translated from the original in Spanish
Experience of good practices
Quality management and its impact on the efficiency of accounting services
La gestión de la calidad y su impacto en la eficacia de los servicios contables
Gestão da qualidade e seu impacto na eficácia dos serviços contábeis
Darian Samá Muñoz1  0000-0002-7380-6115
0000-0002-7380-6115  tdsama1991@gmail.com
tdsama1991@gmail.com
Eduardo Iglesias Fidalgo2  0009-0005-7853-6846
0009-0005-7853-6846  acerco@nauta.cu
acerco@nauta.cu
Viviana Sánchez Muñoz2  0009-0002-1331-8766
0009-0002-1331-8766  viviana.acerco@gmail.com
viviana.acerco@gmail.com
1 Agrarian University of Havana "Fructuoso Rodríguez Pérez". San José de las
Lajas, Mayabeque, Cuba.
2 Non-Agricultural Holding and Management Cooperative Acerco. La Habana, Cuba.
Received: 19/11/2022
Accepted: 11/12/2023
ABSTRACT
The analysis offers a vision of the need for the quality management system as a strategic decision that can help improve performance, provide a solid basis for sustainable development initiatives, the correct realization of processes and efficiency in services. This article shows the experience of the Bookkeeping and Management Cooperative Acerco in documenting and standardizing the processes of its quality management system, the way in which some of the requirements of the standard have been approached and the advantages of this. For this purpose, the International Organization for Standardization's 9001 standard of 2015, the organization's diagnostic methods and methodological elements of popular education are articulated, with a view to implementing a quality management system that has an impact on its members, customers and suppliers, consolidating its strengths and improving its weaknesses, seeking continuous improvement.
Keywords: quality management system; popular education; service processes.
RESUMEN
El análisis ofrece una visión de la necesidad del sistema de gestión de la calidad como decisión estratégica que puede ayudar a mejorar el desempeño, proporcionar una base sólida para las iniciativas de desarrollo sostenible, la correcta realización de los procesos y la eficacia en los servicios. El presente artículo muestra la experiencia de la Cooperativa de Teneduría y Gestión Acerco para la documentación y estandarización de los procesos de su sistema de gestión de la calidad, la manera como han sido enfocados algunos de los requerimientos de la norma y las ventajas de este. Para ello se articulan la norma 9001 del 2015 de la Organización Internacional de Normalización, los métodos de diagnóstico de la organización y elementos metodológicos de la educación popular, con vistas a implementar un sistema de gestión de la calidad que impacte en sus socios, clientes y proveedores, que afiance sus fortalezas y mejore las debilidades, buscando la mejora continua.
Palabras clave: sistema de gestión de la calidad; educación popular; procesos de servicio.
RESUMO
A análise fornece uma visão sobre a necessidade do sistema de gestão da qualidade como uma decisão estratégica que pode ajudar a melhorar o desempenho, fornecer uma base sólida para iniciativas de desenvolvimento sustentável, implementação adequada de processos e eficiência nos serviços. Este artigo mostra a experiência da Cooperativa de Contabilidade e gestão Acerco na documentação e padronização dos processos de seu sistema de gestão da qualidade, como alguns dos requisitos da norma foram abordados e as vantagens disso. Para isso, são articulados o padrão 9001 de 2015 da Organização Internacional de Normalização, os métodos de diagnóstico da organização e os elementos metodológicos da educação popular, com vistas à implementação de um sistema de gestão da qualidade que impacte seus parceiros, clientes e fornecedores, que consolide seus pontos fortes e melhore os pontos fracos, buscando a melhoria contínua.
Palavras-chave: sistema de gestão da qualidade; educação popular; processos de serviços.
INTRODUCTION
Today, quality management has become a way to continuously improve the performance of an organization, which implies working to satisfy not only the end customer, but all stakeholders.
In that sense, organizations are as effective and efficient as their processes are (González Ortiz, 2016; Hernández Palma et al., 2018; Larios Gómez, 2016; Seoane González et al., 2018) so they become aware, considering how to design, improve and maintain their processes and avoid some common troubles such as: insufficient customer focus, low performance, departmental barriers, useless sub-processes due to lack of global vision, excessive inspections and redundancy (Pincay Morales & Parra Ferié, 2020).
In order to have effective processes, some good practices are: documenting processes, establishing indicators to evaluate their effectiveness, eliminating process defects and ensuring their continuous improvement. If these practices are applied in all the important processes of the company, there will be efficient, effective and adaptable processes (Otálora Luna & Gutiérrez Fernández, 2011).
To achieve these good results, organizations need to manage their activities and resources with the aim of guiding them towards achieving them (Pérez Fernández et al., 2022; Samá Muñoz & Benítez Pérez, 2019), which in turn has led to the need to adopt tools and methodologies that allow organizations to configure their management system (Castell Catalá & de la Nuez Hernández, 2021; Flores Torres et al., 2022).
In Cuba, it must be understood that the situation in which organizations are developing today is not only to understand the need for change, but also to maintain the logic between strategy, culture and processes, in addition to meeting the demands of customers, in such a way that the objectives are met, being of vital importance to develop strategies to strengthen their competitive advantages.
The Bookkeeping and Management Cooperative Acerco is one of the non-agricultural cooperatives approved in the country to provide accounting services. It is about to celebrate eight years since its creation, and its members intend to strengthen its internal management system by designing and implementing its quality management system.
They recognize that the adoption of a Quality Management System (QMS) ensures efficiency and effectiveness within the organization. Furthermore, it is a strategic decision that can help the entity improve its overall performance and provide a solid foundation for sustainable development initiatives.
Based on empirical research, it was found that, despite having defined all its processes, only 10.36% of the total processes are completely designed. In the analysis of the designed processes, it was found that not all their input elements are considered, such as: applicable legal and regulatory requirements, audit plan and strategic planning, as well as their output elements: analysis of risks and opportunities of the process, results of audits and indicators for measuring effectiveness.
Therefore, the objective of this article is to show the experience of the Bookkeeping and Management Cooperative Acerco in documenting and standardizing the processes of its quality management system.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The predominant type of research is descriptive-explanatory. Descriptive statistics is used. This is based on percentage calculation, arithmetic mean, mode, construction of scales and graphs, as well as the selection, evaluation and processing of indicators.
For its development, different methods and techniques were used, such as:
Theoretical: They allow the interpretation by means of logical thought processes of the information processed statistically or not. The Historical-Logical method made it possible to study all the information about the evolution of quality and its management in the organizations.
The Analysis and Synthesis allowed to analyze and synthesize the bibliography to define the terms related to the QMS.
The Systemic approach facilitated the analysis of the interrelationships that exist between the elements of quality and thus avoids inconsistencies in its design.
Empirical: They allow gathering the necessary information and data from the practices for decision making in the research. The observation and documentary analysis were oriented to the search for relevant information, linked to the conceptual and methodological elements related to the object of the research. The questionnaires and individual interview guides were applied with the objective of obtaining information about the subject matter of the study.
For the development of the study, the type of sampling selected by the authors was non-probabilistic purposive sampling; the population was represented by seven members representing the social bodies of the cooperative under study and 80 members.
The model used to design the Quality Management System is that of the ISO 9001 standard of 2015, based on the organization's diagnostic methods and articulating methodological elements of Popular Education.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Diagnosis of quality management at Acerco
The assessment of the results of each of the methods and techniques used made it possible, based on the different sources of information, to determine the strengths and weaknesses that characterize the object of study:
Strengths:
The deficiencies detected in the diagnosis can be seen in the following figure.
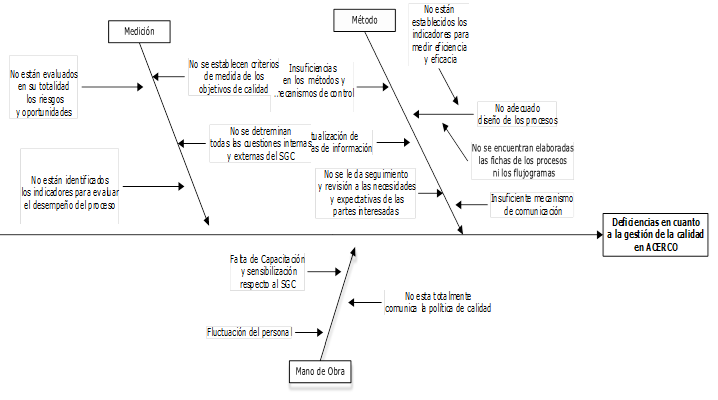
Figure 1. Ishikawa Diagram
Source: Authors' elaboration based on the results of the diagnosis
Quality management system at Acerco
In order to determine the elements of Acerco's QMS, workshops were held and participatory techniques were applied that allowed a collective analysis to understand the current situation of the cooperative, its different components and their complexity, as well as to establish actions and activities in order to plan a strategy aimed at achieving the proposed objectives.
Scope of the quality management system
It covers the processes established in Acerco, in order to offer effective services in terms of accounting, financial and tax solutions that meet the needs and expectations of customers, partners and employees.
From the ISO 9001 standard of 2015, section 8.3 Design and Development is not applicable to the QMS, since the services provided are governed by current accounting regulations that establish the how, in addition, Acerco has defined by identified good practices the know-how for the service processes provided by the organization.
Acerco's process map was drawn up (Figure 2). Of these, four strategic, four substantive and three support processes were classified with a breakdown of their respective activities, and process sheets were drawn up for each process, describing each one to facilitate changes and planning, promoting the use of the process approach and risk-based thinking.

Figure 2. Process map of the Bookkeeping and Management Cooperative Acerco
Source: Joint elaboration based on the workshops held
To verify the relationships between the processes, the level of integration of the processes was established. For this purpose, a survey was made to the heads of processes to evaluate the importance and performance of the relationships between them, resulting in the matrix shown in table 1.
Table 1. Relationships between processes
P1 |
P2 |
P3 |
P4 |
P5 |
P6 |
P7 |
P8 |
P9 |
P10 |
P11 |
P12 |
|
P1 |
I=2 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
|
P2 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
I=2 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
I=2 |
I=2 |
I=2 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
|
P3 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
I=2 |
I=1 |
|
P4 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
|
P5 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
|
P6 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
I=1 |
|
P7 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
|
P8 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
I=1 |
|
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
P9 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
I=2 |
I=2 |
I=2 |
I=1 |
I=1 |
I=1 |
I=3 |
I=1 |
I=3 |
|
P10 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
|
I=3 |
I=3 |
P11 |
I=1 |
I=2 |
I=1 |
I=2 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=3 |
I=2 |
Source: Authors' elaboration
The matrix shows that there are 80 relationships of high importance, none of which is critical. Through this analysis, the level of internal integration of processes (NISDE in Spanish) in Acerco was calculated.
Internal NISDE = 1- (Internal critical ratios / Internal significant ratios)
Internal NISDE = 1- 0/80=1 There is high interrelation between processes
Acerco has decided to design, implement and maintain a QMS that is effective and efficient, with a commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation to new changes in order to achieve the goals proposed in each cycle of its management.
Quality policy at Acerco
To meet the requirements and expectations of partners, customers and employees through the provision of effective management services, integrating accounting, financial and tax solutions that achieve increased satisfaction of stakeholders, focused on the treatment of risks and opportunities, supported by an effective operation of the management system in accordance with the standards, committed to continuous improvement and compliance with applicable legal requirements. For this we have a competent staff, committed to the work and values that distinguish us.
Acerco establishes actions to address risks, responding to the risk management procedure, contained in the risk prevention plans and the opportunities contained in the improvement plans established for each of the processes in the QMS.
It also proposes its quality objectives and the actions to achieve them, deployed in all processes and levels of the cooperative.
Quality objectives at Acerco
The Management Body is ultimately responsible for deploying the policy, scope and objectives of quality, which are analyzed to verify compliance periodically and provides Acerco with the structures and resources necessary for the development of its activities, in order to achieve continuous improvement, sustain and increase the satisfaction of customers, partners and employees as shown in table 2.
Table 2. Responsibilities of the Administrative Body
No |
Processes |
Responsibilities of the Governing Body |
1 |
Strategic planning |
It guides the cooperative towards the fulfillment of the mission, vision and strategic objectives. |
It provides the human, financial and technological resources necessary for the processes to operate efficiently, effectively and with quality. |
||
2 |
Human talent management |
Engages staff to use their skills to achieve objectives. |
Ensures staffing needs to keep them motivated. |
||
3 |
Communication |
Ensures proper communication with customers, partners and collaborators to promote cooperative values, the strengthening of Acerco's image and labor welfare. |
4 |
Measurement, analysis and improvement |
Ensures that quality objectives and quality policy are established, implemented and consistent with the strategic direction. |
Ensures that the requirements of the management system are integrated into the cooperative's processes. |
||
Ensures the integration of all system processes. |
||
5 |
Tangible fixed asset count |
Ensures the monitoring, maintenance, improvement and innovation of processes that add value for the customer. |
6 |
Inventory count |
|
7 |
Account debugging |
|
8 |
Analysis of financial statements |
|
9 |
Economic and financial management |
Maintains healthy economic growth to ensure compliance with strategic objectives. |
10 |
Hiring |
Ensures that customer requirements are correctly identified. |
11 |
Logistics |
Manages the resources necessary for the operation of the cooperative. |
Source: Authors' elaboration
In addition, it ensures the availability of resources and reviews the management system at planned periods to ensure increased customer, partner and employee satisfaction, compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, reasonable assurance in its internal control system, as well as communication channels: whether communication mechanisms were established or strengthened, including:
Design of the Acerco process sheets
For the design of the process sheets, the following steps are established:
Table 3 below shows the results of the work carried out for one of Acerco's QMS processes.
Table 3. Financial Statement Analysis Process Sheet
Process: Analysis of financial statements |
Code: FP-08 |
||||
Objective: To ensure the financial statement analysis service provided by Acerco. |
Head of process: Partner in charge of control and supervision |
||||
Scope: Financial statement analysis service provided by Acerco. |
|||||
Procedures and instructions |
|||||
|
|||||
Associated records |
|||||
|
|||||
Elements of process inputs |
Suppliers |
||||
|
|
||||
Elements of process outputs |
Customers |
||||
|
|
||||
Resources associated with the process |
|||||
Materials/Equipment/Other |
Humans |
||||
Laptop, calculator, sheets, Excel templates, pencil. |
Acerco specialists and technicians. |
||||
Process evaluation indicators |
|||||
Indicator |
Goal |
Calculation method |
Frequency |
Responsible |
|
% of proposed solutions that can be implemented by the partner |
≥95% |
Number of solution proposals implemented / Total solution proposals *100 |
Monthly |
Partner in charge of the activity, branch manager partners |
|
% of customer satisfaction |
≥95% |
(Total number of conformity certificates signed by the client/Total number of clients requesting the service) *100 |
Quarterly |
Partners, branch managers, administrator |
|
Risks associated with the process |
|||||
Risk identification |
Causes of failure |
Shares |
Responsible |
||
Inconsistency or errors in the primary documentation submitted |
|
|
Administrator, partners, branch managers, partners and contractors |
||
Inconsistency in the analysis of detected deviations |
|
|
Partners in charge of the business, branch manager partners |
||
Insufficient proposals for solutions to detected deviations |
|
|
Partners |
||
Failure to verify and correct deficiencies |
|
|
Specialist partner, branch manager partners |
||
Source: Authors' elaboration
Acerco's quality management system is a strategy to increase competitiveness, based on the analysis of processes and indicators as a necessary factor to achieve the satisfaction of its stakeholders; it is the result of articulating the ISO 9001 standard of 2015, with the methods of diagnosis of the organization and the methodological elements of popular education, which allows the collective construction of the system and identify, from good practices, define the interrelationships between the elements that make it up, which enhances its consolidation in terms of mastery by each member of the organization, the role it occupies from an integrative vision, with a view to continuous improvement.
REFERENCES
Castell Catalá, A., & de la Nuez Hernández, D. (2021). Diagnóstico del subsistema calidad en la Unidad Básica de Producción Cooperativa «Julián Alemán». Cooperativismo y Desarrollo, 9(2), 689-711. https://coodes.upr.edu.cu/index.php/coodes/article/view/424
Flores Torres, D. A., Artola Pimentel, M. de L., & Tarifa Lozano, L. (2022). Planificación de la calidad de los procesos en el Instituto Tecnológico Superior Cordillera. Universidad y Sociedad, 14(S2), 76-83. https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/2761
González Ortiz, Ó. C. (2016). Sistema de gestión de calidad: Teoría y práctica bajo la norma ISO 2015. Ecoe Ediciones. https://www.ecoeediciones.mx/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Sistemas-de-gestio%CC%81n-de-calidad-1ra-Edicio%CC%81n.pdf
Hernández Palma, H., Barrios Parejo, I., & Martínez Sierra, D. (2018). Gestión de la calidad: Elemento clave para el desarrollo de las organizaciones. Criterio Libre, 16(28), 169-185. https://doi.org/10.18041/1900-0642/criteriolibre.2018v16n28.2130
ISO. (2015). Sistemas de gestión de la calidad-Requisitos (ISO 9001). International Organization for Standardization. https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:9001:ed-5:v1:en
Larios Gómez, E. (2016). La Gestión de la Competitividad en la MIPYME Mexicana: Diagnóstico Empírico desde la Gestión del Conocimiento. Revista de Administração da Unimep, 14(2), 177-209. http://www.bibliotekevirtual.org/index.php/2013-02-07-03-02-35/2013-02-07-03-03-11/1932-rau/v14n02/20058-la-gestion-de-la-competitividad-en-la-mipyme-mexicana-diagnostico-empirico-desde-la-gestion-del-conocimiento.html
Otálora Luna, J. E., & Gutiérrez Fernández, E. I. (2011). Herramienta de gestión de calidad para el proceso de software, orientada a Mipymes basado en la norma ISO/IEC 15504. Revista Virtual Universidad Católica del Norte, (33), 315-327. https://revistavirtual.ucn.edu.co/index.php/RevistaUCN/article/view/20
Pérez Fernández, D., Urquiola Sánchez, O., & Alpizar Fernández, R. (2022). Sistema de gestión de calidad de la Universidad de Cienfuegos. Universidad y Sociedad, 14(3), 161-169. https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/2853
Pincay Morales, Y. M., & Parra Ferié, C. (2020). Gestión de la calidad en el servicio al cliente de las PYMES comercializadoras. Una mirada en Ecuador. Dominio de las Ciencias, 6(3), 1118-1142. https://www.dominiodelasciencias.com/ojs/index.php/es/article/view/1341
Samá Muñoz, D., & Benítez Pérez, K. (2019). Calidad directiva y su influencia en la productividad. Experiencias de la Empresa de Cemento "Mártires de Artemisa". Folletos Gerenciales, 23(3), 148-159. https://folletosgerenciales.mes.gob.cu/index.php/folletosgerenciales/article/view/211
Seoane González, J. M., Jaya Escobar, A. I., & Guerra Bretaña, R. M. (2018). Proceso de transición a la norma NC-ISO 9001:2015 en la empresa mixta Suchel Camacho S.A. Revista Caribeña de Ciencias Sociales, enero. https://www.eumed.net/rev/caribe/2018/01/empresa-suchel-camachosa.html
Notes
1 Ministry of Finance and Prices of the Republic of Cuba.
2 Cuban Accounting Standard.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Authors' contribution
Darian Samá Muñoz was responsible for the integrity of the work. He contributed with the study and analysis of the conceptual elements, introduction, methodology, results, discussion and review of bibliographic references. He participated in the critical and final revision of the draft article.
Eduardo Iglesias Fidalgo collaborated with the application of the instruments, as well as with the discussion of the research results. He participated in the critical and final revision of the draft article.
Viviana Sánchez Muñoz contributed with the evaluation and discussion of the research results. She participated in the critical and final revision of the draft article.
