 0000-0002-6269-7320
0000-0002-6269-7320  carmenmeme88@gmail.com
carmenmeme88@gmail.comRosa Agnelys Hernández Rodríguez1
 0000-0002-0895-7398
0000-0002-0895-7398  rosyrafa2010@gmail.com
rosyrafa2010@gmail.comImilka Martínez Barreras1
 0000-0001-5027-3523
0000-0001-5027-3523  imilkam@gmail.com
imilkam@gmail.com
Cooperativismo y Desarrollo, May-August 2025; 13(2), e786
Translated from the original in Spanish
Original article
Bibliometric study on tobacco production: references for sustainable local development
Estudio bibliométrico sobre producción del tabaco: referentes para el desarrollo local sostenible
Estudo bibliométrico sobre a produção de tabaco: referências para o desenvolvimento local sustentável
Carmen María Pérez Mendoza1  0000-0002-6269-7320
0000-0002-6269-7320  carmenmeme88@gmail.com
carmenmeme88@gmail.com
Rosa Agnelys Hernández Rodríguez1  0000-0002-0895-7398
0000-0002-0895-7398  rosyrafa2010@gmail.com
rosyrafa2010@gmail.com
Imilka Martínez Barreras1  0000-0001-5027-3523
0000-0001-5027-3523  imilkam@gmail.com
imilkam@gmail.com
1 Information and Technology Management Center of Pinar del Río. Pinar del Río, Cuba.
Received: 3/10/2024
Accepted: 2/06/2025
ABSTRACT
Tobacco is a plant cultivated throughout almost the entire planet. Despite being harmful to human health, its cultivation and preparation means the generation of jobs for thousands of families and a great significance for the economy. For better yields of tobacco crops and greater effectiveness in its processing, the scientific community strives in researches that allow the achievement of superior results. For this reason, the objective of this work was to describe the behavior of scientific publications in Scopus about tobacco production, as a reference to promote sustainable local development. A descriptive, non-experimental, retrospective and descriptive bibliometric study was carried out with a quantitative approach, using theoretical and empirical methods. The results showed that in the study period 2012-2021, the scientific production of this topic increased, with articles predominating among the types of documents, highlighting the authors Baldwin, Fischer, Schillberg and Commandeur, with Baldwin coinciding as the author with the greatest impact on the topic. The journal with the highest number of contributions was Frontiers in Plant Science, while those with the highest impact index were PLoS ONE and Plant Biotechnology Journal. The bibliometric study carried out constituted a reference for entrepreneurs to consult bibliographies on successful experiences in terms of current trends in tobacco production, with the generation of employment, increased income in the communities and the creation of capacities being the most important effects of sustainable local development.
Keywords: tobacco production; bibliometric study; local sustainable development.
RESUMEN
El tabaco es una planta cultivada a lo largo de casi todo el planeta. A pesar de ser nocivo para la salud humana, su cultivo y preparación significan la generación de fuentes de trabajo para miles de familias y un gran significado para la economía. Para mejores rendimientos de los cultivos de tabaco y mayor efectividad en su procesamiento, la comunidad científica se esmera en investigaciones que permitan el logro de resultados superiores. Por tal motivo el trabajo tuvo como objetivo describir el comportamiento de las publicaciones científicas en Scopus acerca de la producción del tabaco, como un referente para impulsar el desarrollo local sostenible. Se realizó un estudio bibliométrico descriptivo no experimental, retrospectivo y con enfoque cuantitativo, utilizando métodos teóricos y empíricos. Los resultados mostraron que en el período de estudio 2012-2021, la producción científica de este tema aumentó, predominando los artículos entre los tipos de documentos, resaltando los autores Baldwin, Fischer, Schillberg y Commandeur, coincidiendo Baldwin como el autor de mayor impacto en el tema. La revista que más contribuciones aportó fue Frontiers in Plant Science, mientras que las de mayor índice de impacto fueron PLoS ONE y Plant Biotechnology Journal. El estudio bibliométrico realizado constituyó un referente para que emprendedores consulten bibliografías sobre experiencias exitosas en cuanto a tendencias actuales sobre la producción del tabaco, siendo la generación de empleo, el incremento de ingresos en las comunidades y la creación de capacidades los efectos de mayor importancia que propicia el desarrollo local sostenible.
Palabras clave: producción de tabaco; estudio bibliométrico; desarrollo local sostenible.
RESUMO
O tabaco é uma planta cultivada em quase todo o planeta. Apesar de ser prejudicial à saúde humana, seu cultivo e preparação significam a geração de fontes de trabalho para milhares de famílias e um grande significado para a economia. Para obter melhores rendimentos das culturas de tabaco e maior eficácia em seu processamento, a comunidade científica se empenha em pesquisas que permitam alcançar resultados superiores. Por esse motivo, o trabalho teve como objetivo descrever o comportamento das publicações científicas no Scopus sobre a produção de tabaco, como referência para impulsionar o desenvolvimento local sustentável. Foi realizado um estudo bibliométrico descritivo não experimental, retrospectivo e com enfoque quantitativo, utilizando métodos teóricos e empíricos. Os resultados mostraram que, no período de estudo de 2012 a 2021, a produção científica sobre esse tema aumentou, com predominância de artigos entre os tipos de documentos, destacando-se os autores Baldwin, Fischer, Schillberg e Commandeur, sendo Baldwin o autor de maior impacto no tema. A revista que mais contribuiu foi a Frontiers in Plant Science, enquanto as de maior índice de impacto foram a PLoS ONE e a Plant Biotechnology Journal. O estudo bibliométrico realizado constituiu uma referência para que os empreendedores consultem bibliografias sobre experiências bem-sucedidas em relação às tendências atuais sobre a produção de tabaco, sendo a geração de empregos, o aumento da renda nas comunidades e a criação de capacidades os efeitos de maior importância que promovem o desenvolvimento local sustentável.
Palavras-chave: produção de tabaco; estudo bibliométrico; desenvolvimento local sustentável.
INTRODUCTION
Local development has gained more and more space in governmental strategies, it is based on economic growth as a primary factor of development. Different approaches to local development have been made throughout history, focusing its attention and broadening the dimensions implicit in its conceptualization. It is closely related to the proactive attitude of the actors of a locality, region or territory to identify and take advantage of the resources provided by the environment in which they develop and to value the endogenous potentialities they have, whether economic or social, cultural, historical, environmental or of any other type that results in local economic development (Zirufo Briones & Pelegrín Entenza, 2023).
The development of human capital is of vital importance to increase technological innovation in agriculture and foster local development, which contributes to benefits for society and the economy, achieves growing and sustainable results, improves food security and the quality of life of the inhabitants (Díaz Gutiérrez, 2020).
Tobacco is a crop that is considered native to the Americas because it was already being cultivated in this region when the Spaniards arrived. It is a plant belonging to the Nicotiana genus of the Solanaceae family, characterized by its large leaves, its large size, and its strong nicotine alkaloids in its leaves. Several varieties of Nicotiana are registered, the two most known and worked by farmers are Nicotiana tabacum with a more pleasant and strong flavor and Nicotiana rustic, with less pleasant flavors. It is cultivated in many developing countries worldwide, where it plays a vital role, from the social and economic point of view, because it is a labor-intensive product, therefore, it is considered a generator of jobs (Enriquez Garcia et al., 2021).
The botanical description according to León Moreno et al. (2020) mentions that it is classified as follows.
Taxonomic classification of the tobacco crop
According to González and Gurdián (1998), tobacco is one of the few crops that reaches the world market entirely based on leaves, it is the most cultivated non-edible commercial plant in the world. For many countries it is of importance in financial and economic policy. Its main use is for smoking, specifically by inhaling its powder.
The production and marketing of cigarettes and other tobacco leaf products involves four stages: raw material production, industrialization, product shaping, distribution and sale.
In charge of transforming tobacco leaf, the tobacco industry (Cortés Hernández et al., 2019), has evolved over time and has been maintained, given that it has adapted to cultural, social and political changes and has favored economic dynamization in the places where it has generated its production.
The industrialization for obtaining products of optimum quality depends on the fulfillment of all the established parameters from the reception of the raw material, its processing, manufacturing, to the final packaging.
The interest of the international scientific community in tobacco production is growing, so it is highly demanded by the actors of the value chain, research that includes soil and seedbed preparation, crop rotation, irrigation, fertilization, pest control, genetic improvement, edaphoclimatic conditions (climate, temperature, humidity), as well as improvements in the industrial process.
Scientific production has also increased, achieving the materialization of the knowledge generated and socialized through information institutions. There are countless journals, databases and platforms that assume this function.
Bibliometrics makes it possible to describe phenomena, trends and regularities that occur in a given field of science (Hernández González et al., 2023), it also studies the quantitative aspects of the production, dissemination and use of the information recorded, for which purpose it develops models and mathematical measures that, in turn, serve to make forecasts and make decisions about these processes (Vargas Leal, 2023).
The indicators used in this discipline constitute necessary scientific tools because they allow the quantification of science in an objective way, since they are enhanced by the explosion of current knowledge and its compilation in bibliographic databases. There is no doubt that, despite the objections that can and should be made, bibliometric indicators facilitate the understanding of research activity (Camps, 2008).
Taking into account the importance of the subject worldwide, the following article aims to describe the behavior of scientific publications in Scopus on tobacco production, as a reference to promote sustainable local development.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The bibliometric study is a descriptive, non-experimental, retrospective study with a predominantly quantitative approach.
Non-experimental: The variables are not intentionally manipulated; the behavior of these variables is observed as they are manifested in their natural context.
Descriptive: It evaluates and collects data on different variables, aspects or dimensions of the phenomenon to be investigated.
Quantitative: because the researcher collected mainly numerical data, which he analyzes by means of mathematical-statistical procedures. There is no influence of the researcher on the phenomena observed.
According to the fundamental objective of the study, the following research methods were used.
For information processing, Microsoft Excel 2007 was used, contemplating as fundamental fields: authors, author code (ID), affiliation, title, year of publication, descriptors, number of citations, type of documents and source of information.
The population consisted of 2422 documents on the topic "Tobacco production" (retrieved in Scopus from 2012 to 2021). To determine the sample to be studied, all the documents were reviewed because, despite excluding in the search strategy the terms "health", "treatment", "smoking", publications associated with these topics and of a social nature and applications for the pharmaceutical and energy industry were retrieved. Finally, a sample size of 971 articles was obtained.
For the study, stages were established to facilitate its realization: familiarization with the subject "Tobacco production" and selection of the database, determination of the search strategy and indicators to be used, selection of the sample, processing of the data obtained and analysis of the results.
The research covers the scientific production referring to the thematic Tobacco Production, framed in a period of 10 years from 2012 to 2021 in the Scopus database that constitutes one of the sources of evaluated scientific information of greater coverage and international relevance. Google Scholar was used as another source of information to collect information on authors, journals, institutions and other aspects that required standardization.
The population includes all articles published on the topic "Tobacco production" at the international level, within the Scopus database in the period 2012-2021. The sample is intentional non-probabilistic, in order to select it, articles that did not provide the information according to the proposed objectives were excluded from the population.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The search and retrieval of data was performed, taking into account the subject of interest and using the search equation: (TITLE-ABS-KEY (tobacco AND production) AND NOT TITLE-ABS-KEY (health AND treatment) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (smoking)) AND (LIMIT-TO (OA, "all")) AND (LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2021) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2020) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2019) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2018) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2017) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2016) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2015) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2014) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2013) OR LIMIT-TO (PUBYEAR, 2012))
For the selection of the indicators, it was followed the premises of other bibliometric studies where the behavior of scientific production on various topics has been investigated (Campos Soto et al., 2020), using in this case those related to productivity, dispersion and visibility and impact.
Productivity indicators
Distribution of authors according to productivity levels
Authors were grouped according to the groups proposed by Lotka (Spinak, 1996):
Transience index
Percentage of transitory or occasional authors within the sample analyzed.
Method of calculation: Transience index (TI) = (TA/Ta) * 100 %.
Where: TA: Transitory author, Ta: Total number of authors identified in the sample.
Transitory author (TA): Whose names appear only once in the indexes of bibliographic sources (Spinak, 1996).
Dispersion indicator
Bradford's law: Bradford's law states that a small number of journals, which make up the core, concentrate a similar number of articles as a large number of journals, grouped in areas of greater dispersion (Miranda Arguedas, 1990).
The minimum number of articles that are necessary to define a zone in an ordered list of journals, consistent with Bradford's law, is calculated:
Bradford's Minimum Zone (BMZ) = NR1a / 2
NR1a: Total number of journals producing 1 article
Impact indicators
The impact indicators have been analyzed according to different variables to determine the influence of tobacco production studies in the scientific literature:
In order to measure the impact constituted by the bibliometric study on tobacco production for local development, the procedure was applied (Pérez Mendoza et al., 2016), which starts from the use of the expert method. When obtaining the values of importance granted by the experts, the calculation procedure is carried out, explained below.
Column 1: Effects of applying the proposed measures. Column 2: Weighting given by the experts for each effect. Column 3: Percentage of the starting situation for the analysis. Column 4: Estimated, also in percent, how much the situation should vary once the proposed measures have been applied. Columns 5 and 6: It is calculated, according to the weighting given to each main effect and the relative valuation made, the number of points to be given to each main effect in each situation (5) = (2) ₓ (3) / (4) (6) = (5) ₓ (4) / (3).
Starting from the total sum of points in each situation it is possible to calculate the increase in effectiveness as follows: Projected effectiveness increase = [ (a) / (b) - 1] ₓ 100.
Where:
(a): Points assigned to the projected situation.
(b): Points assigned to the baseline scenario
Calculation and analysis of indicators
Productivity indicators
The scientific production under study shows an increasing trend during the period 2012-2021 (Figure 1, item a), with the highest number of papers in the years 2020 and 2021; however, the increase has not been stable over time. The highest interannual variations in terms of number of papers are shown in 2016 and 2020, when the variation rate expresses the highest values (23.81 and 22.55 %, respectively). The lowest variation rate was in 2013, which showed a value of 20% (Figure 1, item b).
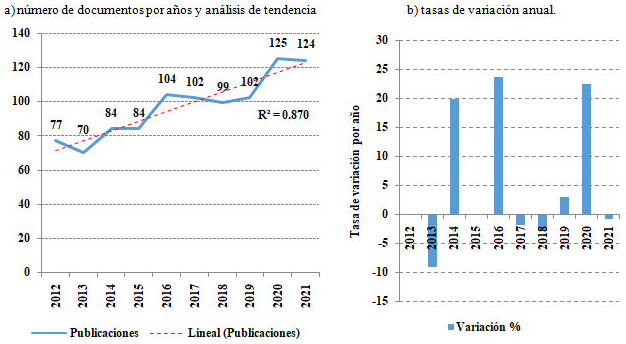
Figure 1. Annual productivity of the subject "Tobacco production" in Scopus from 2012
to 2021
Source: Own elaboration
The format of the publications rescued for the sample is: original articles, conference papers, reviews, book chapters, notes and short articles. 91.8 % correspond to original articles, being the preferred format when writing scientific papers on the subject, followed by conference papers and reviews with 3.6 % and 3.4 % respectively, the rest is represented by 1.2 %.
The number of authors identified in the sample analyzed was 5276, of which 20 (0.37 %) have acted as authors in five or more articles. The researchers with the highest productivity within the thematic area of tobacco production in the period studied were: Baldwin I. T. (12), Fischer R. (11), Schillberg S. and Commandeur U. (7) and Vann M. C., Saito K., McDonald K. A., Buyel J. F. and Menassa R. (6).
It is noteworthy that the most productive authors, highlighting the cases of those occupying positions 1 to 4, did not act as first author in any of their papers. Figure 2 shows their authorship behavior.

Figure 2. Behavior of authors with 5 or more contributions in terms of their role as primary or
secondary author
Source: Own elaboration
Distribution of authors according to productivity levels
Small producers: 4606 (87.30%)
Medium producers: 668 (12.66%)
Large producers: 2 (0.03%)
When analyzing personal productivity, it can be seen that Lotka's law (Spinak, 1996), which states that the bulk of the documents published on a given topic coincide with a very small number of authors who are specialized in that area of knowledge, is fulfilled.
Looking at figure 3, it can be seen that the correlation between the smallest number of authors and the largest number of papers is positive, where at one extreme it is shown that a single author has published 11 and 12 papers on tobacco production and at the opposite extreme 4606 authors have published one.
When examining the linear relationship between the variables, a Pearson correlation coefficient r = -0.51223 is obtained, which indicates that there is a high dependence between the variables and that they have a negative correlation, since they affect each other inversely proportional.
With respect to the coefficient of determination or multiple correlation, the result obtained is R2 = 0.988, which indicates that it has a good fit.
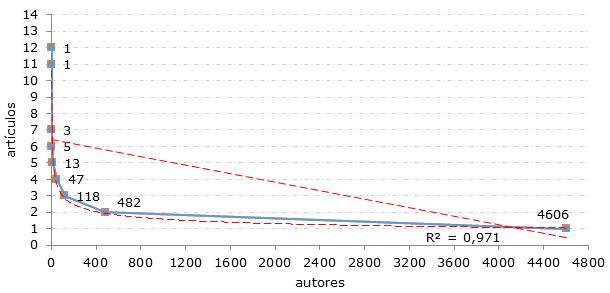
Figure 3. Correlation between the number of authors and the number of articles
on the subject "Tobacco production" in Scopus from 2012 to 2021
Source: Own elaboration
Transitivity index
In the sample, 4606 authors have published only one article, so the Transience Index (TI) was 87.30 %. This value is higher than the 75% suggested by the literature, which is considered high and directly related to low levels of consolidation of the subject analyzed (Spinak, 1996).
In the sample of articles retrieved, 3761 descriptors were identified. The ten most used descriptors were:
As can be seen, tobacco and Nicotiana tabacum are the descriptors that start the list of those most frequently used in the sample analyzed.
A total of 239 journals published at least one article related to tobacco production, which represent more than 1% of the analyzed documents. The most productive journals during the period studied were Frontiers in Plant Science (87), PLoS ONE (80), Plant Biotechnology Journal (61).
Frontiers in Plant Science
Open access multidisciplinary journal, with official publication by the Swiss Frontiers Media. Ranked in quartile 1 of Scopus, in the category, in the period 2012 to 2021, it receives on average, in a time window of 3 years, a total of 38937 citations (Jain et al., 2021).
PLoS ONE
Open access multidisciplinary journal, with official publication by the Public Library of Science of the United States. Ranked in quartile 1 of SCopus, in the category Agricultural and Biological Sciences, Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology, medicine and Multidisciplinary, in the period 2012 to 2021, it receives on average, in a 3-year time window, a total of 188716 citations (Jain et al., 2021).
Plant Biotechnology Journal
Open access, multidisciplinary journal, officially published by Ltd Wiley-Blackwell Publishers, UK. Ranked in quartile 1 of SCopus, in the category Agronomy and Crop Science, Plant Science and Biotechnology in the period 2012 to 2021, it receives on average, in a 3-year time window, a total of 6772 citations.
Dispersion indicators
It describes the quantitative relationship between journals and scientific articles contained in the studied sample, where 971 articles were published in 239 journals and 141 journals have published a single article, calculating the value of the Bradford Minimum Zone yields 70.5.
Once the BMZ was calculated, the list of journals was arranged in descending order of productivity, forming the nucleus those journals that were most productive, whose sum of articles was similar to this value. Consistent with Bradford's law, figure 4 shows that the core is made up of only 1 journal, with 87 articles and 5 dispersion zones, with an average number of articles close to the number of articles in the core.
It can be seen that as the zones move away from the core, the number of journals increases, where, in the most distant one, 224 journals have 79 articles.
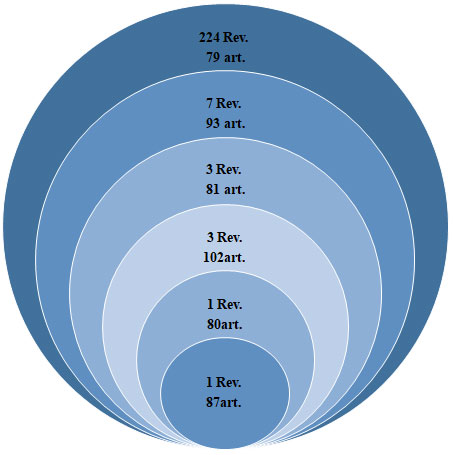
Figure 4. Bradford dispersion area of scientific journals dealing with tobacco production
in Scopus (2012-2021)
Source: Own elaboration
Impact indicators
The most cited papers indexed in Scopus on Tobacco Production in the period 2012-2021 are shown in table 1, appreciating the references with a number of citations greater than 200.
Table 1. Most cited papers on Tobacco production. Period 2012-2021 in Scopus
Authors |
Year of publication |
Title of article |
Journal |
Number of citations |
Kromdijk J., Głowacka K., Leonelli L., Gabilly S. T., Iwai M., Niyogi K. K., Long S. P. |
2016 |
Improving photosynthesis and crop productivity by accelerating recovery from photoprotection |
Science |
574 |
Li F., Pignatta D., Bendix C., Brunkard J. O., Cohn M. M., Tung J., Sun H., Kumar P., Baker B. |
2012 |
MicroRNA regulation of plant innate immune receptors |
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. |
424 |
Mur L. A. J., Mandon J., Persijn S., Cristescu S. M., Moshkov I. E., Novikova G. V., Hall M. A., Harren F. J. M., Hebelstrup K. H., Gupta K. J. |
2013 |
Nitric oxide in plants: An assessment of the current state of knowledge |
AoB PLANTS |
287 |
Glas J. J., Schimmel B. C. J. J., Alba J. M., Escobar-Bravo R., Schuurink R. C., Kant M. R. |
2012 |
Plant glandular trichomes as targets for breeding or engineering of resistance to herbivores |
International Journal of Molecular Sciences |
258 |
South P. F., Cavanagh A. P., Liu H. W., Ort D. R. |
2019 |
Synthetic glycolate metabolism pathways stimulate crop growth and productivity in the field |
Science |
256 |
Lau W., Sattely E. S. |
2015 |
Six enzymes from mayapple that complete the biosynthetic pathway to the etoposide aglycone |
Science |
206 |
Source: Prepared by the authors
The authors who have written the most on the subject in the database analyzed are shown in table 2, where those with more than 6 research have been chosen. In terms of impact, Baldwin I. T. is the author with the highest number of papers (12) and has the highest impact index with 44.5. Saito K. With half of his publications, he has an impact of 40.5, occupying the second place. Schillberg S. is in third place with an index of 29.4. If we review the table, we can see that there is no direct relationship between the number of publications of the author and his impact.
As can be seen, these three authors are considered to be the most specialized in this subject within the Scopus database.
Table 2. Impact index of the most productive authors in the subject. Period 2012-2021 in Scopus
Authors |
Number of documents |
% |
Citations |
I* |
Baldwin I. T. |
12 |
1,24 |
534 |
44,5 |
Fischer R. |
11 |
1,13 |
311 |
28,3 |
Schillberg S. |
7 |
0,72 |
206 |
29,4 |
Commandeur U. |
7 |
0,72 |
105 |
15 |
Vann M. C. |
6 |
0,62 |
15 |
2,5 |
Saito K. |
6 |
0,62 |
243 |
40,5 |
McDonald K. A. |
6 |
0,62 |
147 |
24,5 |
Menassa R. |
6 |
0,62 |
81 |
13,5 |
Buyel J. F. |
6 |
0,62 |
61 |
10,2 |
Source: Prepared by the authors
Table 3 shows the main indexes used by the scientific community to evaluate the impact of authors, articles and journals, in order to determine their relevance in a given area of knowledge (Meriño Morales et al., 2022).
Of the ten most productive journals in the sample, those with the highest H-index are PLoS ONE, Plant Physiology and Journal of Experimental Botany with 367, 329 and 258 respectively, which shows that there is no direct relationship between productivity and the H-index.
Table 3. Impact indexes of the ten most productive journals in the sample (H-index and SRJ)
Journals |
Articles |
H-index |
SJR Index |
Frontiers in Plant Science |
87 |
155 |
1,359 |
PLoS ONE |
80 |
367 |
0,852 |
Plant Biotechnology Journal |
61 |
124 |
2,699 |
International Journal of Molecular Sciences |
41 |
195 |
1,176 |
Plant Disease |
41 |
115 |
0,654 |
Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions |
28 |
160 |
1,099 |
Molecular Plant Pathology |
27 |
114 |
1,619 |
Journal of Experimental Botany |
26 |
258 |
1,913 |
Plant Physiology |
23 |
329 |
2,331 |
Frontiers in Microbiology |
20 |
166 |
1,314 |
Source: Scientific Journal Rankings, 2021
Based on the information provided in table 3, the SJR index is analyzed. Where Plant Biotechnology Journal, Plant Physiology and Journal of Experimental Botany (in descending order) are the journals with the highest index, which translates into higher impact and prestige.
It should be noted that Plant Physiology and Journal of Experimental Botany coincide among the journals with more favorable H and SJR indexes.
Assessment of the impact of the bibliometric study on tobacco production for local development
To carry out the analysis, five experts in information management were selected using the binomial method, who agreed that the main impact provided by this bibliometric study is: To provide tobacco researchers and producers with the journals and articles related to the subject with the highest update and impact to practice and develop their productions, which favors the effects on sustainable local development described in table 4. To begin the analysis, each expert was instructed to rank the items from lowest to highest, with 1 being the most important.
Table 4. Assessment of the effectiveness of the bibliometric study on tobacco production for local development
Effect |
Weighting |
Relative assessment |
Points assigned |
||
Starting situation |
Projected situation |
Starting situation |
Projected situation |
||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
Generation of employment and increased income in communities |
7 |
100 |
160 |
4,37 |
6,99 |
Use of fertilizers to protect the environment |
25 |
100 |
120 |
20,83 |
24,99 |
Enables better use of existing land assets |
18 |
100 |
150 |
12 |
18 |
Increases the quality of negotiations related to costs and risks |
17 |
100 |
130 |
13,07 |
16,99 |
Builds capacity to provide rapid and appropriate responses to development investors |
8 |
100 |
160 |
13,33 |
21,33 |
Total |
|
63,6 |
88,3 |
||
Source: Prepared by the authors
From the assessment made by the experts, it was obtained that the bibliometric study on tobacco production carried out generates an impact of approximately 39% for the sustainable local development.
The bibliometric study on tobacco production carried out constitutes a reference for entrepreneurs to consult bibliographies on successful experiences in terms of current trends in tobacco production.
The generation of employment, the increase of income in the communities and the creation of capacities for quick response to investors are the most important effects that this bibliometric study on tobacco production has on the achievement of sustainable local development.
Scientific production related to tobacco production increased in the study period 2012-2021, with 2020 being the most productive year, with original articles predominating among the types of documents.
The most productive authors were Baldwin I. T., Fischer R., Schillberg S. and Commandeur U. with Baldwin I. T. as the author with the greatest impact on the subject.
The journal with the most contributions was Frontiers in Plant Science, while those with the highest impact indices were PLoS ONE (H Index) and Plant Biotechnology Journal (SJR Index).
Lotka's law and Bradford's law were confirmed as most of the production was concentrated in a small number of authors and journals.
REFERENCES
Campos Soto, N., Navas Parejo, M. R., & Moreno Guerrero, A. J. (2020). Realidad virtual y motivación en el contexto educativo: Estudio bibliométrico de los últimos veinte años de Scopus. Alteridad. Revista de educación, 15(1), 47-60. https://doi.org/10.17163/alt.v15n1.2020.04
Camps, D. (2008). Limits of bibliometrics indicators in biomedical scientific research evaluation. Colombia Medica, 39(1), 74-79. https://doi.org/10.25100/cm.v39i1.552
Cortés Hernández, E. J., Tuta Ramírez, L. T., & García Hurtado, D. (2019). Análisis de la evolución de la industria tabacalera en Ciego de Ávila, Cuba. Universidad & Ciencia, 8(1), 164-174. https://revistas.unica.cu/index.php/uciencia/article/view/1204
Díaz Gutiérrez, D. (2020). El capital humano como principal impulsor del desarrollo local en la innovación tecnológica en la agricultura en Cuba. DELOS: Desarrollo Local Sostenible, 13(37). https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=7794686
Enríquez García, F., Yañez Muñoz, R. M., Oaxaca Arzola, M. G., Barrera Torres, J. C., & Morales Morales, H. A. (2021). Cultivo de Nicotiana tabacum variedad Habanna, en Poza Rica, Veracruz. Revista Biológico Agropecuaria Tuxpan, 9(2), 37-45. https://doi.org/10.47808/revistabioagro.v9i2.367
González, J. M., & Gurdián, W. (1998). Cultivo de Tabaco Nicotiana tabacum L. Escuela Agrícola Panamericana. http://hdl.handle.net/11036/2495
Hernández González, E. A., Landrove Escalona, E. A., Mitjans Hernández, D., Fajardo Quesada, A. J., & Rivera López, S. de las M. (2023). Algunas métricas de los artículos sobre temas de cardiología publicados en la Revista 16 de abril. Revista 16 de abril, 62, e1745. https://rev16deabril.sld.cu/index.php/16_04/article/view/1745
Jain, A., Khor, K. S., Beard, D., Smith, T. O., & Hing, C. B. (2021). Do journals raise their impact factor or SCImago ranking by self-citing in editorials? A bibliometric analysis of trauma and orthopaedic journals. ANZ Journal of Surgery, 91(5), 975-979. https://doi.org/10.1111/ans.16546
León Moreno, C. E., Coronado Silva, R. A., Forero Camacho, C. A., & Roa Rodríguez, M. (2020). Modelo productivo de tabaco (Nicotiana tabacum), variedades Burley y Negro en Santander. Editorial AGROSAVIA. https://editorial.agrosavia.co/index.php/publicaciones/catalog/book/106
Meriño Morales, M. A., Escudero Orozco, C., Monrroy Orozco, S., Morales Ojeda, I., & Campos Muñoz, C. (2022). Uso bioético de las tecnologías de salud en los últimos 20 años: Un estudio bibliométrico en Scopus. Revista Ethika+, (6), 75-95. https://doi.org/10.5354/2452-6037.2022.65869
Miranda Arguedas, A. (1990). Bibliometría. Bibliotecas, 8(1), 1-11. https://www.revistas.una.ac.cr/index.php/bibliotecas/article/view/761
Pérez Mendoza, C. M., Villanzón Sánchez, D. de la C., & Quintana Álvarez, L. (2016). Diseño de procesos del Sistema Logístico de la Universidad de Pinar del Río. Avances, 18(3), 183-191. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=6210094
Spinak, E. (1996). Diccionario enciclopédico de bibliometría, cienciometría e informetría. Unesco. https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000243329
Vargas Leal, V. M. (2023). SPOC de Vigilancia tecnológica, cienciometría y bibliometría dirigido al personal bibliotecario miembro de UNIRED. Universidad Autónoma de Bucaramanga UNAB. http://repositorioslatinoamericanos.uchile.cl/handle/2250/6662001
Zirufo Briones, B. V., & Pelegrín Entenza, N. (2023). Enfoques para caracterizar modelos de desarrollo local que promueven el desarrollo económico, social y ambiental de regiones y comunidades. Mikarimin. Revista Científica Multidisciplinaria, 9(1), 191-210. https://revista.uniandes.edu.ec/ojs/index.php/mikarimin/article/view/3049
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Authors' contribution
Carmen María Pérez Mendoza and Rosa Agnelys Hernández Rodríguez designed the study, analyzed the data, and prepared the draft.
Carmen María Pérez Mendoza and Imilka Martínez Barreras were involved in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data.
All the authors reviewed the writing of the manuscript and approve the version finally submitted.
