 0000-0001-5807-5628
0000-0001-5807-5628  darieldeleongarcia@gmail.com
darieldeleongarcia@gmail.comJesús Suárez Hernández2
 0000-0002-6232-1251
0000-0002-6232-1251  chuchybioenergia2019@gmail.com
chuchybioenergia2019@gmail.comMailyn Esther Castro Premier1
 0000-0002-1109-6461
0000-0002-1109-6461  esthermailyn@gmail.com
esthermailyn@gmail.com
Cooperativismo y Desarrollo, September-December 2024; 12(3), e720
Translated from the original in Spanish
Original article
Strategic Localization of the Sustainable Development Goals. Bibliometric study to guide municipal management
Localización Estratégica de los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible. Estudio bibliométrico de orientación para la gestión municipal
Localização Estratégica dos Objetivos de Desenvolvimento Sustentável. Um estudo bibliométrico para orientar a gestão municipal
Dariel de León García1  0000-0001-5807-5628
0000-0001-5807-5628  darieldeleongarcia@gmail.com
darieldeleongarcia@gmail.com
Jesús Suárez Hernández2  0000-0002-6232-1251
0000-0002-6232-1251  chuchybioenergia2019@gmail.com
chuchybioenergia2019@gmail.com
Mailyn Esther Castro Premier1  0000-0002-1109-6461
0000-0002-1109-6461  esthermailyn@gmail.com
esthermailyn@gmail.com
1 Center for Local and Community Development (Cedel). La Habana, Cuba.
2 University of Matanzas "Camilo Cienfuegos". Indio Hatuey Pasture and Forage Experimental Station. Matanzas, Cuba.
Received: 5/02/2024
Accepted: 11/10/2024
ABSTRACT
In Cuba, the Local Development Strengthening Program has worked on the strategic localization of the Sustainable Development Goals in the country's municipalities. It can be affirmed that local spaces are, ultimately, the key place for provision and development and, as such, local governments are central to the success of sustainable development from municipal management. The present study aims to identify through a bibliometric survey, the contribution of the Strategic Localization of the Sustainable Development Goals to municipal management. The study is based on the analysis of the scientific production available in specialized academic databases between the years 2019 and 2023. The research employed theoretical methods such as analysis and synthesis and hypothetical-deductive, empirical methods, as well as computer and mathematical-statistical tools for data processing. The main result of the study is the identification of guiding aspects that provide municipal management with useful guidelines for action towards 2030.
Keywords: strategic location; sustainable development objectives; municipal management.
RESUMEN
En Cuba el Programa de Fortalecimiento para el Desarrollo Local ha trabajado en la localización estratégica de los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible en municipios del país. Se puede afirmar que los espacios locales son, en última instancia, el lugar clave para la provisión y el desarrollo y, como tales, los gobiernos locales son centrales al éxito del desarrollo sostenible desde la gestión municipal. El presente estudio tiene como objetivo identificar mediante un reconocimiento bibliométrico, la contribución de la Localización Estratégica de los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible a la gestión municipal. El estudio se basa en el análisis de la producción científica disponible en bases de datos académicas especializadas entre los años 2019 y 2023. En la investigación se emplearon métodos teóricos como el análisis y síntesis y el hipotético deductivo, métodos empíricos, así como herramientas informáticas y matemáticas-estadísticas para el procesamiento de los datos. Como principal resultado del estudio se encuentra la identificación de aspectos orientadores que logran ofrecer para la gestión municipal guías útiles para la acción hacia 2030.
Palabras clave: localización estratégica; objetivos de desarrollo sostenible; gestión municipal.
RESUMO
Em Cuba, o Programa de Fortalecimento do Desenvolvimento Local tem trabalhado na localização estratégica dos Objetivos de Desenvolvimento Sustentável nos municípios do país. Pode-se afirmar que os espaços locais são, em última análise, o lugar-chave para a provisão e o desenvolvimento e, como tal, os governos locais são fundamentais para o sucesso do desenvolvimento sustentável a partir da gestão municipal. O presente estudo tem como objetivo identificar, por meio de uma pesquisa bibliométrica, a contribuição da Localização Estratégica dos Objetivos de Desenvolvimento Sustentável para a gestão municipal. O estudo baseia-se na análise da produção científica disponível em bases de dados acadêmicas especializadas entre 2019 e 2023. A pesquisa empregou métodos teóricos, como análise e síntese e métodos hipotético-dedutivos, empíricos, além de ferramentas computacionais e matemático-estatísticas para o processamento dos dados. O principal resultado do estudo é a identificação de aspectos orientadores que conseguem oferecer à gestão municipal diretrizes úteis para a ação até 2030.
Palavras-chave: localização estratégica; objetivos de desenvolvimento sustentável; gestão municipal.
INTRODUCTION
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) - also known as Agenda 2030 - and their 169 targets are far more integrated, comprehensive and complex than the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), contain a better balance between the economic, social and environmental dimensions of sustainable development and provide the opportunity to trigger systemic change towards a sustainable future. This framework is one of the most ambitious and important global agreements in recent history and challenges communities, industries and governments to drive more sustainable development models.
However, while the SDGs help to establish the goals to be achieved by 2030 and to identify indicators and metrics (UN, 2023), the 2030 Agenda says very little about how to implement them, localize them and analyze the impact that public policies can have on them. The long-term planning perspective and the cross-cutting nature of the SDGs pose many challenges for national, regional and local governments in terms of localization, implementation, evaluation, measurement and monitoring. The success or failure of the SDGs depends, to a large extent, on public administration actors, on the one hand, measuring the distance they need to travel to achieve each target and, on the other hand, tracking progress through a combination of metrics (Dizdaroglu, 2017).
The importance that the 2030 Agenda attaches to the local level is precisely one of its main characteristics: all SDGs include targets related to competencies and responsibilities of the municipal sphere, mainly in the provision of basic services and the promotion of entities, and a large part of the 169 SDG targets need to be implemented from the local level to be achieved (Sisto, 2022; Undesa, 2022).
Localizing is the process that considers subnational contexts in the achievement of the 2030 Agenda, that is, from the establishment of goals and targets, to the determination of the means of implementation and the use of indicators to measure and monitor the progress made (Unido, 2023; Villarruel Reynoso & Espinosa Montaño, 2022).
Localization is related to how local and regional governments support the achievement of the SDGs through bottom-up action (Garcia Lopez, 2022) and how the SDGs can provide a framework for local development policy. It can be affirmed that local spaces are ultimately the key place for provision and development and, as such, local governments are central to the success of sustainable development. In Cuba, the Strengthening Municipal Capacities for Local Development project has worked on the Strategic Localization of the SDGs in the country's municipalities (Cedel, 2023).
The present study aims to identify, through a bibliometric survey, the contribution of the Strategic Localization of the SDGs to municipal management.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study is based on the scientific production available in specialized academic databases between 2019 and 2023. For the development of the research, theoretical methods such as analysis and synthesis and deductive hypothetical methods were used. In addition, empirical methods and computer and mathematical-statistical tools such as VOSviewer, IBM SPSS Statistics v.25 and Flourish were used for data processing.
A systematic literature review was conducted based on the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) Statement guidelines, with the intention of covering the minimum set of impact evidence-based articles to be considered for writing systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Research and review articles published in the range 2019 to 2023 were covered. There was no language restriction, in the specialized databases SciELO and ScienceDirect.
The key words used to search for information were: Strategic Localization of the Sustainable Development Goals -LEODS-. Books, papers and theses were discarded from the search because they did not present an impact factor, a relevant condition for the evaluation of the impact of the publications to be included in the study. A total of 500 research and review articles were identified, which were taken with the following criteria: i) that they were from Open Access journals and ii) from areas that include the disciplines of environmental, social and agricultural sciences, energy, engineering and architecture. These references were considered as possible potential studies of the study variable. For the selection of the most relevant documents from these two groups, the methodology offered by the SciELO and ScienceDirect databases was adopted for advanced searches.
A bibliometric analysis with VOSviewer software was used to determine the cooccurrence of words on LEODS and a bibliometric map was constructed to facilitate the visualization of the interrelationship between keywords. Subsequently, a Ward's linkage dendogram was constructed for the keywords on LEODS to determine the most relevant clusters in the analysis of the sources retrieved according to the publication dates in SciELO and ScienceDirect. Subsequently, an analysis is made of the sources retrieved according to their relevance in SciELO and ScienceDirect. The latter shows the main journals identified corresponding to the most relevant articles.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Sustainable Development is understood as: "development that meets the needs of present generations, with the capacity to meet the needs of future generations".
Strategic Localization of the Sustainable Development Goals
The concept of Sustainable Development gained momentum with the Brundtland Report, also known as "Our Common Future", presented by the World Commission on Environment and Development in 1987, which has been reviewed and further developed in different world conferences and summits on Sustainable Development (Rio 92, +10, +20, Johannesburg 2002, among others), ratifying it as the guiding principle for long-term global development and that, to achieve it, it is necessary to balance the three pillars: economic development, social development and environmental protection.
There are contradictory points of view that point to a certain manipulation of these terms. This point is based on arguments that Escobar Freire (2018) and Khan et al. (2023) mention, pointing out, among others, the concepts of the World Bank or the International Monetary Fund such as "sustainable globalization" that "pursues growth with care for the environment" or "sustainable economic growth", respectively. These authors believe that this flexibilization, beyond being of terms, refers to the trend related to neoclassical economic models, considering the natural contrast between "economic growth" and "sustainability", and the improbability of "infinite economic growth in a world with finite resources", a fundamental element of the capitalist system and the market, which makes it necessary to reflect on the new role that the company must assume as part of its management.
On the other hand, the report "The Limits to Growth" (Meadows et al., 1972), mentions the need for a forced change or by humanity's own decisions, in order to avoid possible catastrophes, such as: accelerated industrialization, rapid population growth, widespread malnutrition, depletion of non-renewable resources and environmental deterioration. Similar discussions and analyses are still ongoing, in which the paradigm of sustainability is now urgently incorporated, mainly related to the social sphere and care of the planet (Chaigneau et al., 2022; Massa et al., 2023).
One of the most important achievements is the adoption of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the 17 SDGs by the member states of the United Nations to build a "prosperous, inclusive and just socioeconomic model", which requires the participation of all development stakeholders, including the private sector -business, as a key actor, due to its representativeness and role in the global economy-. Various authors have also made proposals to facilitate the implementation of the SDGs (Govindarajulu et al., 2023), including their interrelated application (Boar et al., 2022).
The implementation of the 2030 Agenda in national and subnational governments represents a form of organized work related to social, environmental and economic development; this requires the commitment of the three levels of government, particularly municipalities (Villarruel Reynoso & Espinosa Montaño, 2022).
Table 1 shows how the 17 SDGs and their 169 targets are much more integrated, comprehensive and complex than the MDGs, contain a better balance between the economic, social and environmental dimensions of sustainable development and provide the opportunity to trigger systemic change towards a sustainable future.
Several lessons were learned from the 2000-2015 period, especially those related to: the basic needs approach to which the MDGs were subscribed, the lack of transparency and participation in the selection of the MDGs, the asymmetry in the distribution of competencies and responsibilities -at the local, national, regional and international levels-, the limitations in the methods for measuring national progress, the restrictions on financing for implementation and the excessive protagonism of the States in the implementation of the agenda to the detriment of other development actors and agents.
Table 1. Comparative aspects of the Sustainable Development Goals and the Millennium Development Goals
Feature |
MDG (2000-2015) |
SDG (2015-2030) |
Number of targets |
8 |
17 |
Number of goals |
21 |
169 |
Approach |
Social Agenda |
Sustainable development: economic growth, social inclusion and environmental protection |
Source: Modified from Escobar Freire (2018)
Strategically localizing the SDGs means striving to include the Integrated Approach to Sustainable Development in all territories, taking into account the particularities of each one of them. In other words, it is time to scale down and also include border areas and regions in multilevel policies for sustainable development. Without forgetting that, and this is fundamental, the SDGs must be prioritized, but not only some territories must be selected for their strategic location, which implies that no territory should be left aside in this process.
According to Abaas and Khalid (2023), the participation of local governments in the implementation of the 2030 Agenda can generate public actions of municipal management with impact, since an important part of them has the territory as its execution space and is related to local spheres. This means building in the long term, since the goals should not be appreciated only in the years of the administration, but the possibility of continuing despite the change of government.
Three experiences of SDG localization in Latin America
Three experiences of localization of the SDGs in three Latin American countries are briefly shown: two at the national level in Colombia and Mexico, as well as a third at the local level in the Metropolitan Region of Belo Horizonte, Brazil.
Colombia: Aligning Territorial Development Plans (PDT) to the SDGs
The country has a High Level Inter-Institutional Commission for the Preparation and Effective Implementation of the 2030 Agenda and its SDGs, chaired by the National Planning Department (DNP) and provides for the participation of actors from academia, the private sector, civil society and the media. The DNP designed the Territorial Kit to provide technical support and "[...] contains the methodologies, tools and guidelines for the formulation of the PDTs, in addition to the guidelines [...] with the SDGs" (DNP, 2017). In addition, to streamline the SDG orientation process in the territorial planning and PDTs, it held meetings through videoconferences with the planning teams of the departmental governors' offices and the mayor's offices of the country's capital cities.
Mexico: Strategy of the Federal Government for a national institutionalization of the 2030 Agenda, integrating subnational authorities
The Office of the Presidency of the Republic, the Executive Commission for the Fulfillment of the 2030 Agenda and the National Institute for Federalism and Municipal Development (INAFED in Spanish), promoted the creation of Follow-up and Monitoring Bodies as "organizational spaces through which state governments join national efforts for the implementation of the SDGs, exchange experiences, coordinate actions and develop monitoring and follow-up mechanisms" (UNDP, 2019).
Its activities include: a) prioritization of 14 SDGs and 25 targets based on the legal competencies of municipal governments; b) application of a technical assistance model by INAFED to monitor the implementation of the SDGs in municipal governments; and c) awareness-raising and training of municipal officials on the 2030 Agenda.
Brazil: the case of the Belo Horizonte Metropolitan Region
The need to advance in the generation of data and indicators to monitor the implementation of the SDGs, both nationally and regionally, has strengthened several multi-stakeholder partnerships in Brazil. At the national and regional level, the work of the Brazilian Civil Society Working Group for the 2030 Agenda and the Metropolitan Observatory of SDGs (METRODS) are relevant. In Belo Horizonte, the ODS em Ação project was promoted in 2017, involving METRODS, Newton Paiva University and Movimento Nossa BH, with financial and technical support from the Thematic Research Network on Data and Statisticsof the United States (Ojeda Medina, 2019).
Analysis of sources retrieved according to publication dates in SciELO and ScienceDirect
Based on the bibliometric map, it was possible to observe the co-occurrence of keywords, based on the title and abstract. The strongest links were established between the terms: sustainability, sustainable development goals and governance. This confirms how important LEODS is in municipal management.
In the bibliometric map (Figure 1), the formation of five clusters (green, yellow, red, blue and magenta) is observed. Most of the terms are found in publications between 2020 and 2021 that group terms from the blue, green and yellow clusters.

Figure 1. Bibliometric map of keywords on LEODS, selected by date
Source: Elaborated based on the processing of selected articles
A hierarchical cluster analysis on the number of occurrences of the terms shows by analyzing the dendogram using a Ward linkage and determining a cut-off at 10, that the terms: (i) strategic objectives, (ii) industry, (iii) human development, (iv) governance, (v) agendas, (vi) agriculture and (vii) circularity, agglomerated in the red cluster, and (viii) sustainable, (ix) sustainable, (x) climate, (xi) development, (xii) mechanics and (xiii) objectives, grouped in the green cluster are relevant in the relationship of LEODS in municipal management (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Dendogram with Ward's linkage for LEODS keywords
Source: Elaborated based on the processing of selected articles
The 500 articles collected on this topic were published between 2019 and 2023. A co-word network composed of three clusters, identified by colors (red, green, blue), was obtained. Within each cluster are the words that relate to the most researched topics on the theme (Figure 3): red cluster with 66 words, green cluster with 44 words and blue cluster with 42 words.

Figure 3. Keyword Network on Strategic Localization of the SDGs
Source: Elaborated based on the processing of selected articles
Of the 46 words with the highest occurrences (greater than 40 occurrences), the words with the highest frequency were: application, reviews, technology, action, region, techniques, practices, changes and policies with 116, 92, 87, 81, 79, 64, 62, 58 and 53 occurrences, respectively (Figure 4).
Analysis of the sources retrieved according to their relevance in SciELO and ScienceDirect
The 300 most relevant sources were taken from the database in the same search terms. From the conformation of the bibliometric map (Figure 5), it was possible to observe the co-occurrence of keywords, based on the title and abstract. Seven clusters were formed (red, green, orange, magenta, blue, yellow and light blue). The strongest links were established between terms such as: sustainable development goals, sustainability, circular economy, sustainable development, climate change and governance. This confirms, once again, how important the Strategic Localization of the Sustainable Development Goals is in municipal management.
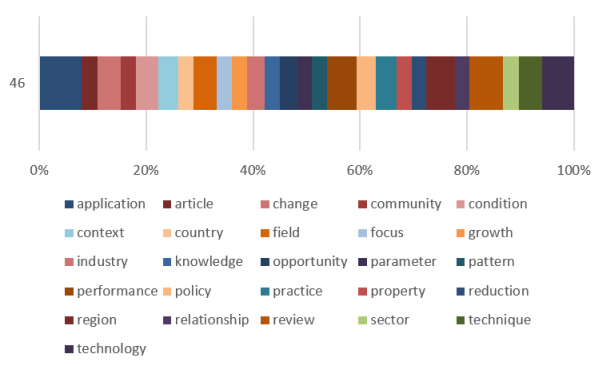
Figure 4. Words with the highest frequency of occurrence
Source: Own elaboration

Figure 5. Bibliometric map of LEODS keywords, selection by relevance
Source: Elaborated based on the processing of selected articles
A network of co-words was obtained, made up of four clusters, composed of 37, 34, 36 and one word. Within each cluster are the words that are related to the most researched topics on the subject. Figure 6 shows the co-word density map based on the title and abstract. Some of the most related keywords are: sustainable development goals, localization, community, opportunities, models, technologies, environmental impact, scenarios, emission, innovation, projects, transition. This reaffirms the importance of LEODS in municipal management.

Figure 6. Density map of the network of co-words on Strategic Localization of the
SDGs, selected by relevance
Source: Elaborated based on the processing of selected articles
Among the journals identified corresponding to the most relevant articles in the SciELO and ScienceDirect databases between 2019 and 2023, Information Fusion stood out, with 38.6 citations and an impact factor (IF) of 18.6, followed by Journal of Cleaner Production and Global Food Security, with 18.5 citations (IF 11.1) and 15.3 citations (IF 8.9), respectively. Journal of Cleaner Production is where the highest number of articles, 34, have been published in relation to the topic of study. Table 2 shows the top 10 journals.
Table 2. Leading journals
Ranking |
Journals |
Publications 2019-2023 |
CiteScore |
FI |
1 |
Information Fusion |
1 |
38.6 |
18.6 |
2 |
Journal of Cleaner Production |
34 |
18.5 |
11.1 |
3 |
Global Food Security |
6 |
15.3 |
8.9 |
4 |
Cities |
25 |
10.4 |
6.7 |
5 |
Ecological Indicators |
10 |
10.3 |
6.9 |
6 |
CIRP Annals |
1 |
9.5 |
4.1 |
7 |
International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction |
23 |
7.4 |
5 |
8 |
Water Security |
1 |
7.1 |
- |
9 |
Geoforum |
21 |
6.8 |
3.5 |
10 |
Climate Risk Management |
11 |
6.7 |
4.4 |
Source: Own elaboration
In the research conducted, there is evidence of a wide use of concepts related to Localization in the SDGs, with sustainability in various sectors and, in particular, in municipal or local management.
The study reveals particular issues of importance for the localization of the SDGs in the management agenda of municipal governments. Having recent scientific trends on LEODS shows that this facilitates the outlining of municipal public policies and also in the adaptation of supra-municipal public policies, such as national policies or those arising from sectors or provinces. The results achieved offer an orientation in terms of themes for LEODS in the formulation of development programs and projects within the framework of the Municipal Development Strategies.
In the authors' assessments and based on their work experience, it is argued that in terms of LEODS, local public administration institutions in Cuba require training and capacity building; the study presented here helps to clarify the routes to be followed in this regard.
This study has its own limitations, due to the sources used for its development and the degree of subjectivity in the parameters chosen for the mathematical processing of the data. The authors consider that studies with similarities in the same subject matter could be carried out, and conclusions related to this study could also be drawn from other sources of information. In any case, this would enrich the proposed objective.
The terms: i) strategic objectives, ii) industry, iii) human development, iv) governance, v) agendas, vi) agriculture and vii) circularity, viii) sustainable, ix) sustainable, x) climate, xi) development, xii) mechanics and xiii) objectives, have a strong relationship in the articles published in the years between 2019 and 2023. On the other hand, from the analysis conducted on the most relevant articles, it is observed that the terms: i) sustainable development objectives, ii) localization, iii) community, iv) opportunities, v) models, vi) technologies, vii) environmental impact, viii) scenarios, ix) emission, x) innovation, xi) projects and xii) transition are the most related with respect to their co-occurrence. Of the 46 words with the highest occurrence in the texts of titles, keywords and abstracts, those with the highest frequency were: i) application, ii) reviews, iii) technology, iv) action, v) region, vi) techniques, vii) practices, viii) changes and viii) policies, which exceed 53 occurrences. The above allows affirming that there is a contribution to municipal management in the period 2019-2023 from research results that have been published in journals, with presence in the SciELO and ScienceDirect databases on Strategic Localization of Development Objectives.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Thanks for the support provided in the research process to the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (COSUDE), to the team of the International Project: Strengthening of Municipal Capacities for Local Development, which contributed with more than 150 people who formed the municipal teams, and to the team of the Project associated with the National Local Development Program in Cuba: "Tools for the management, monitoring and evaluation of municipal development strategies in Cuba".
REFERENCES
Abaas, Z. R., & Khalid, Z. (2023). Towards local sustainability: A case study to evaluate outdoor urban spaces in Baghdad using physiological equivalent temperature index. City and Environment Interactions, 20, 100115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cacint.2023.100115
Boar, A., Palau Pinyana, E., & Oliveras-Villanueva, M. (2022). Alternatives to solve SDG trade-offs and to enforce SDG synergies: A systematic literature review. Management of Environmental Quality: An International Journal, 33(2), 478-493. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-07-2021-0181
Cedel. (2023). Guía de orientaciones para la localización de los ODS en municipios cubanos. Centro de Desarrollo Local y Comunitario.
Chaigneau, T., Coulthard, S., Daw, T. M., Szaboova, L., Camfield, L., Chapin, F. S., Gasper, D., Gurney, G. G., Hicks, C. C., Ibrahim, M., James, T., Jones, L., Matthews, N., McQuistan, C., Reyers, B., & Brown, K. (2022). Reconciling well-being and resilience for sustainable development. Nature Sustainability, 5, 287-293. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-021-00790-8
Dizdaroglu, D. (2017). The Role of Indicator-Based Sustainability Assessment in Policy and the Decision-Making Process: A Review and Outlook. Sustainability, 9(6), 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9061018
DNP. (2017). Inclusión de los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible en los planes de desarrollo territoriales, 2016-2019. Departamento Nacional de Planeamiento. https://observatorioplanificacion.cepal.org/es/modalidades/inclusion-de-los-objetivos-de-desarrollo-sostenible-en-los-planes-de-desarrollo
Escobar Freire, V. (2018). Los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible (ODSs), los Principios del Pacto Global de Naciones Unidas y la Responsabilidad Social Corporativa, desafíos y oportunidades. Universidad Técnica Particular de Loja. https://dspace.utpl.edu.ec/handle/20.500.11962/22269?mode=full
García López, J. (2022). Los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible en las ciudades españolas: Contribuciones para su evaluación a través de indicadores [Tesis doctoral, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid]. https://doi.org/10.20868/UPM.thesis.70175
Govindarajulu, D., Gupta, D., & Prakash, A. (2023). Barriers and opportunities in achieving climate and sustainable development goals in India: A multilevel analysis. Journal of Integrative Environmental Sciences, 20(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1080/1943815X.2022.2163665
Khan, S. A., Al Rashid, A., & Koç, M. (2023). Adaptive response for climate change challenges for small and vulnerable coastal area (SVCA) countries: Qatar perspective. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 96, 103969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2023.103969
Massa, I., Marinescu, S., Fuller, G., Bermont Díaz, L., & Lafortune, G. (2023). Sustainable Development Report for Small Islands Developing States 2023. Sustainable Development Solutions Network. https://sdgtransformationcenter.org/reports/sustainable-development-report-for-small-island-developing-states-2023
Meadows, D. H., Meadows, D. L., Randers, J., & Behrens, W. W. (1972). Los Límites del Crecimiento. Informe al club de Roma sobre el predicamento de la humanidad. Universe Books. https://www.library.dartmouth.edu/digital/digital-collections/limits-growth
Ojeda Medina, T. (2019). El rol estratégico de los gobiernos locales y regionales en la implementación de la Agenda 2030: Experiencias desde la cooperación Sur-Sur y Triangular. OASIS, (31), 9-29. https://doi.org/10.18601/16577558.n31.03
Sisto, R. (2022). Diseño y aplicación de una metodología de análisis de impacto de las políticas públicas sobre los objetivos de desarrollo sostenible [Tesis doctoral, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid]. https://doi.org/10.20868/UPM.thesis.70174
UN. (2023). Global Sustainable Development Report 2023: Times of crisis, times of change: Science for accelerating transformations to sustainable development (Independent Group of Scientists appointed by the Secretary-General). United Nations. https://sdgs.un.org/gsdr/gsdr2023
Undesa. (2022). SDG Good Practices: A compilation of success stories and lessons learned in SDG Implementation. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. https://sdgs.un.org/publications/sdg-good-practices-2nd-edition-2022
UNDP. (2019). Localización de la Agenda 2030 en México. Sistematización de la instalación y operacionalización de los Órganos de Seguimiento e Instrumentación de la Agenda 2030. Programa de Naciones Unidas para el Desarrollo. https://www.undp.org/es/mexico/publicaciones/localizacion-de-la-agenda-2030-en-mexico
Unido. (2023). Statistical Indicators of Inclusive and Sustainable Industrialization. SDG 9 Progress Report 2023. United Nations Industrial Development Organization. https://stat.unido.org/publications/statistical-indicators-inclusive-and-sustainable-industrialization-biennial-progress
Villarruel Reynoso, D., & Espinosa Montaño, M. (2022). Localización de las Agendas de Desarrollo Global en el Área Metropolitana de Guadalajara. En La marca Guadalajara. Estrategias de posicionamiento frente al COVID-19 durante el 2020-2021 (pp. 57-73). Universidad de Guadalajara. https://puntoscardinales.com.mx/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Marca-GDL-GDL.pdf
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Authors' contribution
Dariel de León García and Jesús Suárez Hernández designed the study, analyzed the data and prepared the draft.
Mailyn Esther Castro Premier was involved in the collection, analysis and interpretation of the data.
All the authors reviewed the writing of the manuscript and approve the version finally submitted.
