 0009-0005-4803-6429
0009-0005-4803-6429  ymelgarejo485@gmail.com
ymelgarejo485@gmail.comSoleydi Rivero Amador2
 0000-0001-9015-4748
0000-0001-9015-4748  soly@upr.edu.cu
soly@upr.edu.cuYimian de Liz Contreras Díaz2
 0000-0002-0557-6768
0000-0002-0557-6768  yliz@upr.edu.cu
yliz@upr.edu.cu
Cooperativismo y Desarrollo, January-April 2024; 12(1), e686
Translated from the original in Spanish
Original article
Information Management for strategic decision making. Actions to develop a procedure at the institutional level
Gestión de Información para tomar decisiones estratégicas. Acciones para desarrollar un procedimiento a nivel institucional
Gestão de Informação para tomada de decisões estratégicas. Ações para desenvolver um procedimento em nível institucional
Yanisleydi Melgarejo Hernández1  0009-0005-4803-6429
0009-0005-4803-6429  ymelgarejo485@gmail.com
ymelgarejo485@gmail.com
Soleydi Rivero Amador2  0000-0001-9015-4748
0000-0001-9015-4748  soly@upr.edu.cu
soly@upr.edu.cu
Yimian de Liz Contreras Díaz2  0000-0002-0557-6768
0000-0002-0557-6768  yliz@upr.edu.cu
yliz@upr.edu.cu
1 Consolación del Sur Tobacco and Integral Company. Consolación del Sur, Pinar del Río, Cuba.
2 University of Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saíz Montes de Oca". Pinar del Río, Cuba.
Received: 13/11/2023
Accepted: 26/01/2024
ABSTRACT
The modern organization faces a constant evolution of management principles towards the management of intangibles, capable of generating sustainable competitive advantages over time. The strategic management of information and knowledge comes to light as tools for disseminating other fundamental processes and systems within the organization. This research carries out an exploratory study of the informational context of a Cuban state company, based on the study of theoretical references related to Information Management and its contribution to strategic decision making. By applying empirical methods in this informational context, a set of actions is projected to form a procedure for Information Management in strategic decision making. The energizing effect of the activity of managers in Information Management as a tool for strategic decision making is ratified, as well as the need for the systemic interaction of three fundamental dimensions: people, processes and technologies.
Keywords: business management; information management; strategic decision making.
RESUMEN
La organización moderna se enfrenta a una evolución constante de los principios de gestión hacia la gerencia de intangibles, capaces de generar ventajas competitivas sostenibles en el tiempo. Surge a la luz la gestión estratégica de la información y el conocimiento como herramientas diseminadoras de otros procesos y sistemas fundamentales dentro de la organización. La presente investigación realiza un estudio exploratorio del contexto informacional de una empresa estatal cubana, partiendo del estudio de referentes teóricos relacionados con la Gestión de Información y su contribución en la toma de decisiones estratégicas. Mediante la aplicación de métodos empíricos en este contexto informacional se proyecta un conjunto de acciones para conformar un procedimiento para la Gestión de Información en la toma de decisiones estratégicas. Se ratifica el efecto dinamizador de la actividad de los directivos en la Gestión de Información como herramienta de la toma de decisiones estratégicas, así como la necesidad de la interacción sistémica de tres dimensiones fundamentales: las personas, los procesos y las tecnologías.
Palabras clave: dirección empresarial; gestión de información; toma de decisiones estratégicas.
RESUMO
A organização moderna enfrenta uma constante evolução dos princípios gerenciais em direção à gestão de intangíveis, capaz de gerar vantagens competitivas sustentáveis ao longo do tempo. A gestão estratégica da informação e do conhecimento está surgindo como uma ferramenta para a disseminação de outros processos e sistemas fundamentais dentro da organização. A presente pesquisa realiza um estudo exploratório do contexto informacional de uma empresa estatal cubana, com base no estudo de referências teóricas relacionadas à Gestão da Informação e sua contribuição para a tomada de decisões estratégicas. Por meio da aplicação de métodos empíricos nesse contexto informacional, projeta-se um conjunto de ações para formar um procedimento de Gestão da Informação na tomada de decisões estratégicas. Ratifica-se o efeito dinamizador da atividade dos gestores na Gestão da Informação como ferramenta para a tomada de decisões estratégicas e a necessidade da interação sistêmica de três dimensões fundamentais: pessoas, processos e tecnologias.
Palavras-chave: gestão empresarial; gestão da informação; tomada de decisões estratégicas.
INTRODUCTION
With the current development of the Information and Knowledge Society, intangible resources occupy a relevant and increasingly leading place in institutional and regional development. In the business context, this paradigm presupposes the incorporation of new models, methodologies, tools and methods for the management of organizational processes, which contribute to the increase in effectiveness in decision-making and favor the harmonious use of management methods in interaction with the management of intangible resources that provide added value to business processes (Andreu et al., 1991; Rodríguez Cruz & Pinto Molina, 2018).
The importance of information for organizations lies in the fact that they use it when carrying out their daily operations and strategically in the search for competitiveness. In this sense, a very valid option to increase the value of this important resource is to integrate it and have it available at the right time so that it can be analyzed by decision makers. The operational and strategic management of this resource continues to be of vital relevance in the current context in which technological tools play a very important role by integrating data as raw material of information and increasing the value that it provides for the company.
Cuban state companies are engaged in the creation of a new direction and management system in accordance with the Guidelines of the Economic and Social Policy of the Party and the Revolution and the updating of the Cuban Economic Model. This process has a fundamental antecedent: The Business Improvement Process that began more than 15 years ago. This management system requires a systemic analysis of the company to achieve transformations that increase economic efficiency and achieve a higher level of competitiveness.
The Information System, one of the subsystems of this improvement process in state companies, has constituted a precedent of Information Management (IM), recognized by Cuban managers, from the standards established in the resolution of Decree Law 281, of 2011. The methodological experiences implemented in the last 10 years have not achieved sufficient methodological and practical tools to manage information harmoniously and in correspondence with business contexts (Artiles Visbal & Márquez Pérez, 2013; Barrera Rodríguez & Blanco Rosales, 2019). In this way, the development and adaptation of methodological tools to achieve a relevant and developing IM continues to be a pending issue in Cuban state companies. Likewise, every type of social institution needs optimal mechanisms to manage information as an essential resource for decision making.
This research aims to carry out an exploratory study of the informational context of a Cuban state company, based on the study of theoretical references related to IM and its contribution to strategic decision making. By applying empirical methods in this informational context, a set of actions are projected to form a procedure for IM in strategic decision making.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The research applied several theoretical methods, such as: the Historical-logical, the Systemic-structural, the Analysis-synthesis and finally the Inductive-deductive method to develop logical reasoning that allows reaching general conclusions adjusted to the context, based on experiences reflected in the scientific literature and background of studies on these topics in the business sector and at the institutional level.
In addition, empirical methods were applied from the use of Document Analysis to delimit theoretical and conceptual references that support the research work to the application of empirical techniques, such as interviews and surveys, to describe the informational context of a Cuban state company. To obtain evidence about the behavior of IM in the company under study, interviews and surveys were used as empirical techniques for collecting information for the research.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Theoretical references of the research
In the bibliographic study of the topic, IM experiences were identified from the Cuban business context, although the majority come from non-business institutions. But the results obtained have implementation levels favorable to the business environment (Macías Mesa et al., 2020; Ponjuán Dante, 2018).
These methodological approaches that integrate IM and the decision-making process show the insufficiency of methodological mechanisms that integrate the role of the manager in the informational processes of the organization at the different hierarchical levels (strategic, administrative and operational) of management. In the business context, the critical issues of the practical implementation of IM can be identified in: recognizing the determining role of the manager (Contreras Díaz et al., 2021), the diagnosis of information needs (Núñez Paula, 2004) and the conceptualization of specific patterns to the study of the internal and external context of strategic decision making (Huber, 1989). Furthermore, it is considered essential to gear the company's information policy to the determination of information needs, the search and retrieval of relevant information for decision making, the storage, dissemination and use of information and the design of useful information flows for decision making. With the marked intention of structuring the information according to the hierarchical levels of management, strategic decisions are oriented in the scope of action of the strategic level of management as the driving entity of the rest of the management levels.
The research appropriates the approaches of: Citroen (2011) and Rodríguez Cruz and Pinto Molina (2018) to characterize strategic decision making according to the patterns established by IM. From these references, the following aspects are assumed that distinguish the decision-making process:
Main methodological approaches for business Information Management
From the methodological point of view, IM at the business level, although it happens in a similar way in other types of institutions, is related to the components of Information Systems (IS), business processes, their behavior, as well as the interrelation with the environment that surrounds the company. The following aspects, declared by Ponjuán Dante (2008), constitute fundamental guides to establish methodological patterns:
These essential aspects to methodologically manage information resources are taken up by Hernández González et al. (2020) by founding a procedure for IM at tactical and operational management levels, this study being a reference for this research. The evident intrinsic relationship between IS and IM is materialized in the conceptualization of this type of management, especially from the strategic perspective. This research is oriented in this sense, focusing its attention on the strategic levels of business management.
Likewise, this management requires a close interaction between business processes and subsystems, the following factors can become determinants in the efficiency and effectiveness of the results of this activity (Artiles Visbal & Márquez Pérez, 2013; Ponjuán Dante, 2008; Woodman, 1985):
Currently, despite the high increase in computer tools and high levels of informational competencies of users, these problems persist in information management. The need for methodological proposals from systemic perspectives is reaffirmed, without ignoring the information infrastructure of the institution, the characteristics of decision makers when using information, as well as the structural and functional conditions of the organization at its decision levels (Rodríguez Cruz & Pinto Molina, 2018).
An element to consider is the fact that IM occurs in the context of an organization, no two are alike, so each one designs and develops this type of management under its own conditions, with its own components and scope. Furthermore, every organization demands information because it is essential for its activities, functions, goals and objectives. This resource is one of those that gives you the vitality to sustain and develop; therefore, it must be placed at the highest level of institutional priority. An organization will always be able to improve if its members have the capabilities and skills to work with information and know how to precisely define their needs and secondly if it achieves the optimal functioning of the components of a harmonious system for IM, in the organizational context.
In the scientific literature consulted, research that proposes models for IM stands out, from various scopes or approaches and, although they are not specifically applied in the business sector, they do have relevant contributions to achieve the objective pursued by this research. The methodological approaches of IM are expressed in the design of various IS focused on the management of operational, tactical or strategic information. Methodological approaches for information auditing are also distinguished.
The research is based on the study carried out by Hernández González et al. (2020), in which methodological studies in the scientific literature are segmented into three types of approaches:
Methodological approaches: Models
Widely generalized methodological approaches are distinguished in Cuban companies that were in the Business Improvement Process and contributed to the creation of Information Systems to face this process of change at the business level. In this regard, the "Information and Knowledge Management Model for the company in improvement (MOGICEP in Spanish)" proposed by Artiles Visbal and Márquez Pérez (2013), uses knowledge management as a managerial approach, it is based on the country's regulatory framework to the organization of information, its application is based on the fulfillment of the design stages of the information system within business management. The limitations of this model are expressed from its orientation only to Cuban companies that are in the Improvement Process to its concentration on an Information System that ignores components and attributes that articulate the informational structure of a company from its strategic dimension, which is what promotes the proper execution of the information process life cycle. That is to say, transcendental aspects of the business management process and its three levels are neglected: operational, tactical or strategic.
Another distinctive methodological approach is the proposal of Ruiz González (2016): "MOPIGD: Model for the implementation of document management in the Cuban business system". This author establishes the methodological guidelines to follow to implement the documentation and archives law of the Republic of Cuba at the business level. It establishes methodological patterns of IM and its relationship with Document Management. This proposal is very specific for the documentation process at the business level, but it provides laudable aspects to establish patterns in IM at the business level, which is why it is a highly recognized precedent for this research.
One of the most significant experiences in the national informational context is the one proposed by Rodríguez Cruz and Pinto Molina (2018) with their "Information use model for strategic decision making in information organizations". This model, although it has been validated in institutions that produce information for the society they serve, is intensely guided by the Prescriptive Theory of decision making, proposed by Meacham (2004), which emphasizes the ways that decision makers should and can develop to make decisions appropriately. It describes from three fundamental dimensions: the informational dimension of the environment of the strategic decision-making process, the behavioral dimension regarding the use of information and the contextual dimension. This last dimension is an important background to take into account when designing methodological tools in the business context, which is why it is an important reference for this research.
Methodological approaches: Information systems design
Viteri Guzmán (2021) proposes a Management Information System in companies in the agricultural sector. The formation of this management system is implemented in the Argentine agricultural sector, which is why it provides experiences of its implementation in this type of companies. Although only the accounting process and its information flow are underway, the main structures of a harmonious IS can be identified within a business context. This research constitutes a very representative precedent to take into account in the methodological implementation of IM in companies in the agricultural sector.
Sierra Flores et al. (2021) design an Information System aimed at decision-making at the Finlay Vaccine Institute and other Cuban scientific institutions. In the implementation of this system, it is possible to diagram the process flows within the entity under study. Although this proposal manages to incorporate information flows into the value chain of this scientific institution, the actions taken to incorporate IM in strategic decision making are still insufficient. This research addresses IM as an integrative process to the designed system and although it does not go into specific steps or stages for IM, it establishes certain relevant aspects in this type of management at the business level.
Methodological approaches: Procedures, methodologies or strategies
González Guitián et al. (2017) establish an "Integrative methodology of information and knowledge auditing for organizations", this tool integrates the audit of information and knowledge in an organizational context. It is focused on various types of institutions and manages to identify, inventory and map information resources and their flows, as well as assess the processes associated with their management. It integrates the diagnosis and evaluation of information and knowledge management together and in its implementation it can be adapted to the specific characteristics of any organization. This proposal provides a very important guide to establish the audit of information, but there remain transcendental aspects unaddressed in relation to the functions of managers or decision-makers and their role in the information process, especially in relation to the processes within the organizational structures of companies. It is a very distinctive reference for the present research in relation to the inventory of information resources in the business context.
From an approach related to education, Gamboa Graus et al. (2021) developed a procedure that distinguishes the relevance of IM as a competence of school administration. The authors study in depth the informational competencies of users to achieve efficient IM. A set of steps are structured that, although they do not have direct application to the business sector, provide several aspects to keep in mind to bring together fundamental elements of IM: users, technologies and processes. Emphasis is placed on the informational competencies of users.
The methodological approaches of this work constitute an important background to establish company-level actions for IM in strategic decision making. Although there is a variety of methodological designs that integrate IM and the decision-making process, there is still no methodological mechanism that integrates the role of the manager in the informational processes of the organization, in order to interrelate the information flows that derive from the departmental areas, at the different hierarchical levels (strategic, administrative and operational) of management, with the legal regulations regarding information and its internal control.
Study of the informational context in the Consolación del Sur Comprehensive and Tobacco Company
Taylor (1982) justified the importance of studying informational environments to understand the value of information as a management and decision-making resource. In this sense, the consumer of information is the one who can assign the true value of this intangible resource. The present research takes up this traditional and highly current approach to assert that understanding this environment would give managers a better appreciation of the value of information in a specific context. It is agreed with Ponjuán Dante (2017), by highlighting this approach and by defining informational context as:
That organizational space established by the limits established by the policies and regulations of the institution or country, where informational and knowledge processes are developed based on compliance with the corporate reason of that space. Therefore, it can be an institution, a community, or any group that, for social reasons (ages, interests, etc.) is grouped together with a certain objective.
At the current moment that Cuban society is experiencing, in order to achieve pertinent computerization in parallel with an improvement in management and decision-making, it is necessary to study the informational contexts to establish the management of the information resource from its strategic impact on the organizational environment. Within the institutions, the IMS constitutes the linking element and the pillar on which each type of management rests in all subsystems at the institutional level, as well as the objectives set in each area or system of the organization. Various types of IS are required, adjusted to different contexts, various forms of implementation with a logical interaction and fluidity of information in the processes or subsystems of the organization. Just as formalized information management is also needed as an essential resource to achieve integration in the management of business subsystems.
This research studies the informational context of the Consolación del Sur Integral and Tobacco Company, in the Province of Pinar del Río. It is started from its main objectives and reason for being before society to distinguish the main regularities that affect the correspondence: individual-technology-institutional processes in IM practices.
The social mission of this company is related to satisfying the demands of various crops and other productions, collecting and processing tobacco, in function of the development of the province, through efficient, competitive and sustainable performance. It is one of the leading companies in the territory, due to its economic importance and size. In its structure it is made up of: 14 Base Business Units and works in coordination with a total of 27 Credit and services Cooperatives, 9 Agricultural Production Cooperatives and a Basic Cooperative Production Unit.
Distinctive aspects of the company diagnosis
After triangulation of the information obtained through the application of a survey, interviews and documentary analysis it is managed to describe the informational context of this company. A set of irregularities can be raised that influence the Information Management in the Consolación del Sur Comprehensive and Tobacco Company:
The diagnosis carried out allowed to identify a set of irregularities that influence the IM of the company under study, the most relevant being: the incorrect design of information flows in all departmental areas, the excess of information, dispersed and duplicated, and the little flexibility in information formats. The main weakness in information processing is identified as the exclusive use of operational information systems, leaving information related to the tactical and strategic levels of management unprocessed. Information systems focused on decisions are not considered timely, which affects the systemic and methodological interaction of IM in all subsystems of the company. Although managers recognize the importance of information as a decision-making resource, methodological patterns or informational policies are not established for its management in correspondence with strategic decision-making.
Main actions to form an IM procedure in strategic decision making
The methodological actions of IM at the business level, in correspondence with strategic decisions, must be implemented systematically at strategic levels and in interaction with the rest of the management levels. Interacted phases must be established and grouped into three fundamental moments: planning the type of strategic decisions to be executed, processing the necessary information and analyzing possible options to be executed.
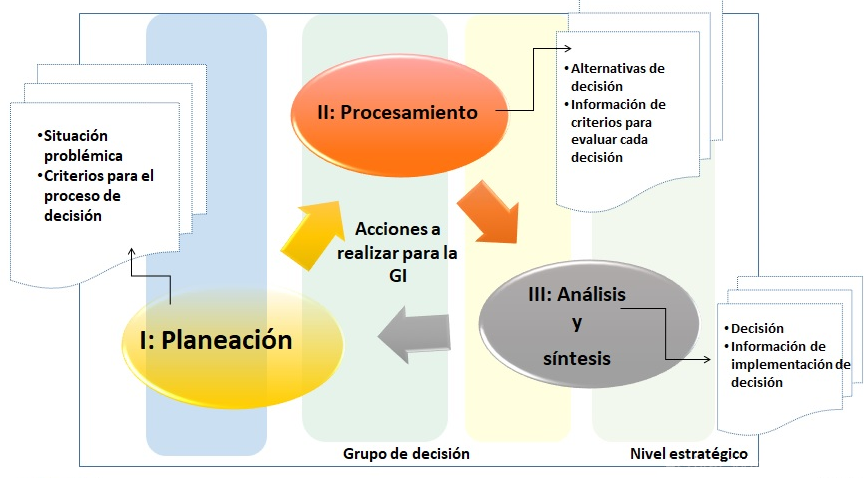
Figure 1. Main phases to form actions in the IM for strategic decision making
Source: Own elaboration
A first phase of planning is proposed that establishes the main actions related to the plan to follow in the search for information, followed by information processing actions and closing in a third phase of analysis and synthesis of the information obtained. In this way, those involved in decision-making in a business context carry out an informational process that is more adjusted to the contingencies related to the strategic decision to be made (Figure 1).
The actions, although segmented in a logical order, have a systemic interaction in their procedure; the following are proposed:
Decision processes in the business context have intrinsic characteristics associated with particular components, among which are: problem-situation, the individual, information and contextual elements. According to each level of business management decision, these components acquire different qualities, which is why it is very favorable to establish methodological patterns to develop Information Management in an integrated, harmonious and systematic manner that allows establishing information systems relevant to the social task. of the institution.
In the context of the Cuban state company, despite there being regulations to establish Information Management, it is insufficient the managers' understanding of the methodological and tooling issues of this management as a developer of the decision-making process and contributor of added value to the functions.
The diagnosis carried out in the company under study expressed the need to establish patterns in Information Management in the decision-making process, with emphasis on strategic ones. The need to form an Information Management System that establishes methods and ways of managing information in business processes is reaffirmed, from the functions of each member of the company and the use of appropriate information technologies.
REFERENCES
Andreu, R., Ricart, J. E., & Valor, J. (1991). Estrategia y sistemas de información. McGraw-Hill.
Artiles Visbal, S., & Márquez Pérez, Y. (2013). El Modelo de Gestión de Información y Conocimiento: Resultados de su aplicación en una empresa en perfeccionamiento. GECONTEC: Revista Internacional de Gestión del Conocimiento y la Tecnología, 1(1), 13-23. https://www.upo.es/revistas/index.php/gecontec/article/view/448
Barrera Rodríguez, S., & Blanco Rosales, H. (2019). Reflexiones sobre una futura ley de empresas para Cuba. COFIN Habana, 13(1). https://revistas.uh.cu/cofinhab/article/view/865
Citroen, C. L. (2011). The role of information in strategic decision-making. International Journal of Information Management, 31(6), 493-501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2011.02.005
Contreras Díaz, Y. de L., Rivero Amador, S., González Pérez, M., & Ding, B. (2021). La Gestión de Información en el contexto institucional y el rol de los directivos. Revista Cubana de Información En Ciencias de La Salud, 32(1), e1798. https://acimed.sld.cu/index.php/acimed/article/view/1798
Gamboa Graus, M. E., Castillo Rojas, Y., & Parra Rodríguez, J. F. (2021). Procedimiento para la gestión de información en función de la administración escolar. Dilemas contemporáneos: Educación, Política y Valores, 8(3). https://doi.org/10.46377/dilemas.v8i3.2625
González Guitián, M. V., Pinto Molina, M., & Ponjuán Dante, G. (2017). Metodología integradora de la auditoría de la información y el conocimiento para organizaciones. Revista Cubana de Información en Ciencias de la Salud, 28(1), 60-76. https://acimed.sld.cu/index.php/acimed/article/view/1033
Hernández González, Y., Contreras Díaz, Y. de L., Rivero Amador, S., & Carpio Vento, M. (2020). Acciones para la gestión de información en la toma de decisiones desde las funciones de los directivos en el contexto empresarial. Revista de estudios económicos y empresariales, (32), 59-68. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=8131093
Huber, G. P. (1989). Toma de decisiones en la gerencia (2.a ed.). Trillas. https://etrillas.mx/libro/toma-de-decisiones-en-la-gerencia_2396
Macías Mesa, J. A., Artola Pimentel, M. de L., Macías Gallardo, M., & Tarifa Lozano, L. (2020). Análisis de la dirección estratégica como activo de la gestión organizacional. Revista Cubana de Administración Pública y Empresarial, 4(2), 225-238. https://apye.esceg.cu/index.php/apye/article/view/131
Meacham, B. J. (2004). Decision-Making for Fire Risk Problems: A Review of Challenges and Tools. Journal of Fire Protection Engineering, 14(2), 149-168. https://doi.org/10.1177/1042391504040262
Núñez Paula, I. (2004). AMIGA: Una metodología integral para la determinación y la satisfacción dinámica de las necesidades de formación e información en las organizaciones y comunidades. Revista Cubana de Información en Ciencias de la Salud, 12(4). http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S1024-94352004000400002&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=es
Ponjuán Dante, G. (2008). Gestión de información: Precisiones conceptuales a partir de sus orígenes. Informação & Informação, 13(1esp), 26-38. https://doi.org/10.5433/1981-8920.2008v13n1espp26
Ponjuán Dante, G. (2017). Aproximaciones al estudio de contextos informacionales de instituciones cubanas del sector de educación superior. Palabra Clave (La Plata), 7(1), e035. https://doi.org/10.24215/18539912e035
Ponjuán Dante, G. (2018). La información y el conocimiento como recursos organizacionales en Cuba: Algunos aportes sobre este proceso desde la academia. Bibliotecas. Anales de Investigación, 14(Extra 1), 73-81. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=6312038
Rodríguez Cruz, Y., & Pinto Molina, M. (2018). Modelo de uso de información para la toma de decisiones estratégicas en organizaciones de información. Transinformação, 30(1), 51-64. https://doi.org/10.1590/2318-08892018000100005
Ruiz González, M. de los Á., Sánchez Vignau, B. S., & Bodes Bas, A. (2016). MOPIGD: Modelo para la implementación de la gestión de documentos en el sistema empresarial cubano. GECONTEC: Revista Internacional de Gestión del Conocimiento y la Tecnología, 4(2), 52-68. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7506463
Sierra Flores, M. M., Calero Ramos, R., Guzmán Sánchez, M. V., Toledo Roy, J. C., & Gamboa Calderón, Y. G. (2021). SIGI, un sistema integral de información cienciométrica y curricular para instituciones de investigación-enseñanza. Investigación Bibliotecológica: archivonomía, bibliotecología e información, 35(89), 111. https://doi.org/10.22201/iibi.24488321xe.2021.89.58431
Taylor, R. S. (1982). Value Added Processes in the Information Life Cycle. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 33(5), 341-346. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.4630330517
Viteri Guzmán, G. K. (2021). Sistema de información gerencial para el control de costos de empresas agroindustriales del cantón Daule. Universidad y Sociedad, 13(5), 605-614. https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/2271
Woodman, L. (1985). Information Management in Large Organizations. En B. Cronin, Information Management: From Strategies to Action. Aslib.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Authors' contribution
All authors reviewed the writing of the manuscript and approve the version finally submitted.
