 https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0190-1030
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0190-1030 maylen.alfonso@upr.edu.cu
maylen.alfonso@upr.edu.cu
Cooperativismo y Desarrollo, January-April 2021; 9(1), 243-257
Translated from the original in Spanish
Redesign of the adventure tourism modality in the nature destination Viñales
Rediseño de la modalidad de turismo de aventura en el destino de naturaleza Viñales
Redesenho da modalidade de turismo de aventura no destino natural de Viñales
Maylén Alfonso Dovale1; Claudia María González Slovasevich2; Iverilys Pérez Hernández3
1 Universidad de Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saíz Montes de Oca". Facultad de Ciencias
Económicas y Empresariales. Pinar del Río, Cuba.
 https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0190-1030
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0190-1030
 maylen.alfonso@upr.edu.cu
maylen.alfonso@upr.edu.cu
2 Universidad de Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saíz Montes de Oca". Facultad de Ciencias
Económicas y Empresariales. Pinar del Río, Cuba.
 https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5853-429X
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5853-429X
 claudia.slovasevich@upr.edu.cu
claudia.slovasevich@upr.edu.cu
3 Universidad de Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saíz Montes de Oca". Facultad de Ciencias
Económicas y Empresariales. Pinar del Río, Cuba.
 https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2124-0962
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2124-0962
 iverilys@upr.edu.cu
iverilys@upr.edu.cu
Received: 19/09/2020
Accepted: 20/04/2021
ABSTRACT
Cuba's tourism offer has diversified with the strength of nature tourism. In this sense, it is essential to know in detail the motivations that allow defining the characteristics of this market segment. The present work was carried out in the tourist destination of Viñales; in it, the adventure tourism product was redesigned, taking advantage of the natural goodness and potentialities that the destination possesses, from the application of a methodology, which objective was to organize the adventure tourism product in the destination Viñales, contributing to increase the levels of average stay, to diversify the portfolio of products and to improve the indicators of the life cycle of the destination. In the research theoretical and empirical methods were used that facilitated the verification of the problematic situation and the solution in the redesign of the product, sustained by the bibliographic support used. The research provided important elements for making commercial decisions in relation to the consolidation of the adventure modality; on the other hand, the redesign was focused on the adventure market segment, responding to its demands.
Keywords: tourism; nature tourism; adventure tourism; tourism product
RESUMEN
La oferta turística en Cuba se ha diversificado con la fortaleza del turismo de naturaleza. En este sentido, es fundamental conocer en detalle las motivaciones que permiten definir las características de este segmento de mercado. El presente trabajo se realizó en el destino turístico de Viñales; en el mismo, fue rediseñado el producto de turismo de aventura, aprovechando las bondades y potencialidades naturales que posee el destino, a partir de la aplicación de una metodología, cuyo objetivo consistió en organizar el producto turístico de aventura en el destino Viñales, contribuyendo a aumentar los niveles de estancia promedio, a diversificar la cartera de productos y a mejorar los indicadores del ciclo de vida del destino. En la investigación, fueron utilizados métodos teóricos y empíricos que facilitaron la constatación de la situación problémica y la solución en el rediseño del producto, apoyado en el soporte bibliográfico utilizado. La investigación aportó elementos importantes para tomar decisiones comerciales en relación con la consolidación de la modalidad de aventura; por otra parte, el rediseño fue enfocado al segmento de mercado de aventura, respondiendo a las exigencias de este.
Palabras clave: turismo; turismo de naturaleza; turismo de aventura; producto turístico
RESUMO
A oferta turística em Cuba se diversificou com a força do turismo de natureza. Neste sentido, é imprescindível conhecer em detalhe as motivações que permitem definir as características deste segmento de mercado. O presente trabalho foi realizado no destino turístico de Viñales; nele, o produto de turismo de aventura foi redesenhado, aproveitando os benefícios naturais e potenciais que o destino tem, a partir da aplicação de uma metodologia, cujo objetivo era organizar o produto de turismo de aventura no destino Viñales, contribuindo para aumentar a permanência média níveis, diversificar o portfólio de produtos e melhorar os indicadores de ciclo de vida do destino. Na pesquisa, foram utilizados métodos teóricos e empíricos que facilitaram a verificação da situação problema e a solução no redesenho do produto, apoiados no suporte bibliográfico utilizado. A investigação contribuiu com elementos importantes para a tomada de decisões comerciais em relação à consolidação da modalidade de aventura; por outro lado, o redesenho foi focado no segmento de mercado de aventura, respondendo às suas demandas.
Palavras-chave: turismo; turismo de natureza; turismo de aventura; produto turístico
INTRODUCTION
There are various interpretations of tourism; one of them is that of Gurría Di-Bella (1991), who refers to how "Tourism is an abstraction, a concept of which we all have different interpretations" (p. 13). He highlights how each definition is valid, regardless of its approach and analyzes the etymology of this word which "comes from tour or turn, derived from the Latin verb tornare which in turn derives from the noun tornus, meaning to return, turn or return; in short, it means to go and return" (p. 14). On the other hand, Cardet, Palao and González (2018), emphasize that the real wealth of tourism, more than in the impact of the economic growth of a country, is in the strong traces that, in visitors, culture and traditions leave.
There are different forms of tourism. In this regard, Pérez and Villa (2011) summarize the classification of tourism modalities according to the purpose of the trip, which includes the adventure tourism category, belonging to the alternative tourism modality. Osorio (2016) points out how tourism and adventure represent an opportunity for the conservation of cultural heritage. Díaz cited in Carvache et al. (2018) refers to its origin as part of a growth in demand towards activities, with certain levels of risks in natural environments. In the case of adventure tourism, several authors have defined it. Among them, Progen (1979), Ewert (1989), Johnston (1992), Eagles (1995), Smith and Jenner (1999), Ceballos-Lascurain (2000), cited in Moral, Cañero and Orgaz (2013). One of the most recent definitions is provided by the World Tourism Organization (2019, p. 37) states that:
Adventure tourism is a type of tourism that normally takes place in destinations with specific geographic characteristics and landscapes and tends to be associated with physical activity, cultural exchange, interaction and closeness to nature. This experience may involve some type of real or perceived risk and may require significant physical and/or mental exertion.
In this sense, given the growing relevance and demand for it, it is essential to know in detail the motivations that allow defining the characteristics of this market segment, taking into account that the motivation of this typology corresponds to the participation in spaces that offer the possibility of risk, managed with adrenaline-provoking activities. From this, it will be possible to analyze the steps for the design of the adventure modality, through the product design methodology of Gómez (2014) and which are the most important actions to address from the point of view of product conception.
That is why the research is carried out in the Viñales destination, based on the conceptual analysis and the particularities of this modality, with the purpose of fulfilling the problem. The tourist destination of Viñales does not have within its product portfolio the modality of adventure in an organized, coherent and integrated way according to the existing potentialities. As an object of this study, the following is proposed: Tourism product management process and as a field of action: the management of tourism products in the modality of adventure in Viñales destination. The general objective to organize the adventure tourism product in the Viñales destination that contributes to increase the levels of average stay, to diversify the product portfolio and to improve the indicators of the life cycle of the destination.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In the research, theoretical and empirical methods were used, in order to determine the most essential components in the movement and context in which the phenomenon under analysis develops. Among them, the dialectical-materialist method stands out as the guiding method, since it allows interpreting the development process of the object of study in its evolution.
Theoretical methods
Empirical methods
The methodology developed for the empirical diagnosis of the design of adventure tourism products is based on fundamental information needs such as: identifying the levels of knowledge regarding the topic under research, the tourism potential of the municipality and the limitations for the implementation of adventure tourism products.
For the general characterization of the municipality of Viñales and the current economic-productive and service structure of the locality, the information provided by Physical Planning 2014, Onat 2017 was used, an analysis of the process of updating the Cuban economic model where the importance of tourism is highlighted, from the Guidelines (209, 210, 211, 212, 213, 213, 214, 215, 216) of the VI Congress of the PCC (2017) was carried out. In addition, secondary information sources and primary information sources were used as instruments.
The secondary source of information, composed of documentary analysis, gathers the regulatory legal framework, the life cycle of the Viñales destination, the Mintur commercial report, the escalation file, the commercial report of the Ecotur and Cubanacán 2019 travel agency, Mintur 2019, Commercial Office Cubanacán 2019 Travel Agency, the statistical report of the non-state sector linked to tourism.
The primary sources of information used in the research are based on the analysis of empirical methods for measurement. The survey was used, which was applied to lessors in the non-state sector. To determine the sample, the population constituted by the total number of renters in the municipality, which amounts to 1,358 rental houses grouping a total of 2,382 rooms, was assessed. The SAMPLE program was applied where, for the aforementioned population and with a margin of error of 10%, the result of the sample to be applied was a total of 90 surveys. A survey was dedicated to foreign clients, where the population was estimated as the number of international tourists who arrived at the Viñales facilities of the Palmares extra-hotel chain in the last five years, for an average of 367 852. The SAMPLE program was applied, where, for a margin of error of 5%, the result of the sample to be applied was a total of 384. The data resulting from all the surveys were processed by the statistical program SPSS, version 22.0.
The interview was also used, which can be classified as semi-structured and individual. Interviews were conducted with the president of the Municipal Administration Council, the sub-delegate of Mintur in Pinar del Río, the commercial director of Palmares in Pinar del Río, the director of the Rancho San Vicente Hotel in Viñales and the climbing guides of the municipality under study.
The information was triangulated from the most relevant elements resulting from the information sources. The Vester Matrix was applied to rank the problems or restrictions that were determined from all the information sources developed, finally listing a group of potentialities and restrictions in the municipality for the development of adventure tourism products: canopy, climbing and jeep safari.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
De la Ballina (2017) mentions the evolution of marketing, firstly, focused on sales and later, aimed at providing value and satisfaction to customers. Gurría Di-Bella (1991) refers how the process of commercialization of tourism services is carried out by tourism marketing. According to Díez Santo (2011) quoted by Muro and Saravia (2019, p. 57), this term is understood as "(...) a set of services, composed of a combination of elements that present a series of differentiating characteristics specific to the tourist activity (...)".
To address the design of tourism products, there are currently different methodologies, including those of: Gómez (2014); Nasimba and Cejas (2015), Saravia and Muro (2016).
Tourism products: methodology for their elaboration
After analyzing the methodologies, the authors consider that for the redesign of the adventure product in the Viñales destination, the most relevant is that of Gómez (2014).
In order to adequately develop the methodology, the authors consider it necessary to determine the principles that govern a harmonious and sustainable development, which will govern the tourism activity specialized in the adventure modality, which are: complementarity, integration, coherence and harmony, adventure-nature and uniqueness.
Phase I. Inventory of tourist attractions
The first step of this phase consisted of updating the inventory of attractions present for the adventure modality in the study area.
According to Gómez (2014), experts consider that tourism resources should be constituted as tourism attractions through a technical process so that they contribute efficiently to the design of tourism products.
The analysis developed from primary and secondary information sources corroborated that not all the potentialities of the attractions of the place are taken advantage of in the conception of the adventure product for a market whose tendency moves towards the search for experiences and the stimulation of adrenaline, through its immersion in nature.
The attractions of the place were evaluated in a workshop by tourism specialists (specialists of the Viñales National Park, commercial staff of the Mintur delegation, professors of tourism management and specialties of the Mintur Training Center in the province, specialists of the heritage office, tourist guides of the travel agencies of the province), recognizing that there are attractions of relevance for the development of the adventure modality and to add value to it, such as the historical and cultural resources.
In general, the main attractions for the development of the adventure modality are summarized as follows:
In summary, Viñales has potential for the development of products that respond to the adventure modality, in the enjoyment of trekking, climbing, canopy, jeep safari and canopy, with different degrees of difficulty.
Definition of activities to be developed (Phase II. Product redesign)
The type of activity that the tourist can carry out linked to it is identified, establishing the time it would take to carry out each one of them. This step is vital, since it will later allow the design of an itinerary that will serve as the basis for the offer that will make up the modality and on which the needs of services and equipment to carry them out can be built.
Trekking 1 The Great Viñales National Park Hike
The trekking "La Gran caminata del Parque Nacional Viñales" is a tour that has three stages with a stay of five days and four nights. It has four interpretative stops, day and night observation of the flora and fauna. The general level of difficulty is medium and the total distance to be covered is about 106 km.
Trekking 2 Trekking with cyclotourism Mountain, Wildlife and Communities
This proposal is a hike with seven interpretive stops, which takes place in areas of Viñales National Park. The route begins and ends at the "La Esmeralda" farm; the rustic campsites have not yet been completed. The estimated distance is 86 km, combining walking with cycling.
Jeep Safari A summit of adventure
The tour proposes an adventure trip with two jeeps, between the intramontane valleys that border the Viñales National Park, with ten stops and the program combines the development of canopy. The proposal includes a three-day and two-night stay for up to four guests. The route is about 100 km long.
Canopy Tour Viñales
The use and enjoyment of the canopy circuit by tourists is done from the 1st to the 5th platform, accompanied by trained guides for this type of modality. The tour extends about 1,200 meters. Once the circuit is finished, tourists can enjoy some refreshments in the service area. The speed is from 20 to 30 km/hour, the route is 800 meters long, and the time of the tour is from 20 minutes to 1 hour.
Climbing
To this activity, no adaptations are developed, it is only considered that there are all the conditions to develop this product; it can be combined with trekking, canopy, jeep safari and climbing. The altitude ranges from 50 to 250 meters in the sectors cuerda la vaca and la costanera respectively. The product "Adventures among Jurassic mogotes" satisfies your recreational needs, combining the activities of trekking, canopy, jeep safari and climbing.
Once the main ideas were selected, the authors outlined the concept of the Adventure product "adventures through prehistory": which is the result of the harmonious combination of the natural and historical-cultural attractions present in this physical space, with the needs and motivations of the main international and national segments that visit the facility in search of adventure in nature and our roots for the pleasure of adrenaline, entertainment and relaxation.
The concept product of "Adventures among Jurassic mogotes" is represented by the following diagram (Fig. 1).
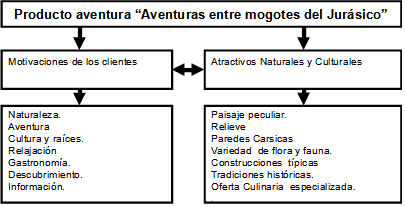
Fig. 1 - Diagram of "Adventures among Jurassic mogotes"
Source: Own elaboration
It is considered a product that in its redesign allows customers.
The main users of the product will be:
German, French, Italian, English, English, Dutch, Belgian, national clients, etc. with motivations or inclinations towards adventure in nature and culture, who like to visit the camps looking for an experience.
The product must become a unique experience in the territory due to its singular attractions.
The new proposal is conceived as an improved product, based on the previous one, but enriching it, taking advantage of the potential of the natural and cultural attractions, providing added value to achieve customer satisfaction.
As a result of the redesign of the Jurassic mogotes adventures product, a more comprehensive and differentiated product was achieved based on the use of the natural and cultural attractions of the place, which responds to the demands of customers visiting the region.
The redesigned product is conceived with the articulation of lodging and restaurant services, oriented towards the possibility of productive linkages, revitalizing natural and cultural attractions.
REFERENCES
Cardet Fernández, E., Palao Fuentes, R., & González Sainz, Y. (2018). Procedimiento para el diseño de productos turísticos basados en el patrimonio de un municipio. Retos de la Dirección, 12(1). https://revistas.reduc.edu.cu/index.php/retos/article/view/2203
Carvache Franco, W., Carvache Franco, M., Carvache Franco, O., & Recalde Lino, X. (2018). Preferencias para el turismo de aventura en la elaboración de un paquete turístico: Caso Santa Elena, Ecuador. Revista Interamericana de Ambiente y Turismo, 14(1), 43-51. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-235X2018000100065
de la Ballina Ballina, F. J. (2017). Marketing turístico aplicado. ESIC Editorial. http://www.marcialpons.es/libros/marketing-turistico-aplicado/9788417024628/
Gómez Ceballos, G. (2014). Procedimiento metodológico de diseño de productos turísticos para facilitar nuevos emprendimientos. RETOS. Revista de Ciencias de la Administración y Economía, 4(8), 158-171. https://doi.org/10.17163/ret.n8.2014.08
Gurría Di-Bella, M. (1991). Introducción al turismo. Trillas. https://asesoresenturismoperu.wordpress.com/2019/03/21/introduccion-al-turismo-2/
Ibáñez Pérez, R. M., & Cabrera Villa, C. (2011). Teoría General del Turismo: Un enfoque global y nacional. Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur. https://books.google.com.cu/books/about/Teor%C3%ADa_general_del_turismo.html?id=VN_CMwEACAAJ
Moral Cuadra, S., Cañero Morales, P., & Orgaz Agüera, F. (2013). El turismo de aventura: Concepto, evolución, características y mercado meta. El caso de Andalucía. Facultad de Turismo y Finanzas. https://idus.us.es/handle/11441/52975
Muro, M. N., & Saravia, M. del C. (2019). Tourist products methodology for its elaboration: Cultural and historical product in the coast district, Buenos Aires province, Argentine Republic. Journal of Tourism and Heritage Research, 2(1), 123-156. http://www.jthr.es/index.php/journal/article/view/34
Nasimba, C. M., & Cejas, M. F. (2015). Diseño de productos turísticos y sus facilidades. Qualitas, 10, 22-39. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nasimba-Maribel/publication/333221285_Articulo_de_revision_DISENO_DE_PRODUCTOS_TURISTICOS_Y_SUS_FACILIDADES/links/5ce2cde7299bf14d95aa8667/Articulo-de-revision-DISENO-DE-PRODUCTOS-TURISTICOS-Y -SUS-FACILIDADES.pdf?origin=publication_detail
Osorio Osorio, J. A. (2016). La aventura del turismo; revivificando la cultura a través del turismo y el patrimonio. International Journal of Scientific Management and Tourism, 2(2), 285-295. http://www.ijosmt.com/index.php/ijosmt/article/view/107
PCC. (2017). Lineamientos de la Política Económica y Social del Partido y la Revolución para el período 2016-2021. Partido Comunista de Cuba. VII Congreso. http://www.granma.cu/file/pdf/gaceta/Lineamientos%202016-2021%20Versi%C3%B3n%20Final.pdf
Saravia, M. del C., & Muro, M. N. (2016). Productos turísticos. Metodología para su elaboración. Revista de Ciencias Sociales, 8(29), 53-78. http://www.unq.edu.ar/advf/documentos/593819f510992.pdf
UNWTO. (2019). UNWTO Tourism Definitions. World Tourism Organization (UNWTO). https://doi.org/10.18111/9789284420858
Conflict of interest:
Authors declare not to have any conflict of interest.
Authors' contribution:
Maylén Alfonso Dovale and Iverilys Pérez Hernández contributed in the conception, study design, data collection, analysis and interpretation.
Claudia María González Slovasevich was involved in the collection, analysis and interpretation of the data, as well as the drafting of the manuscript.
All authors reviewed the writing of the manuscript and approve the version finally submitted.
